动态数据导出是一般项目都会涉及到的功能。它的基本实现逻辑就是从mysql查询数据,加载到内存,然后从内存创建excel或者csv,以流的形式响应给前端。
- 参考:https://grokonez.com/spring-framework/spring-boot/excel-file-download-from-springboot-restapi-apache-poi-mysql。
SpringBoot下载excel基本都是这么干。
虽然这是个可行的方案,然而一旦mysql数据量太大,达到十万级,百万级,千万级,大规模数据加载到内存必然会引起OutofMemoryError。
要考虑如何避免OOM,一般有两个方面的思路。
一方面就是尽量不做呗,先怼产品下面几个问题啊:
- 我们为什么要导出这么多数据呢?谁傻到去看这么大的数据啊,这个设计是不是合理的呢?
- 怎么做好权限控制?百万级数据导出你确定不会泄露商业机密?
- 如果要导出百万级数据,那为什么不直接找大数据或者DBA来干呢?然后以邮件形式传递不行吗?
- 为什么要通过后端的逻辑来实现,不考虑时间成本,流量成本吗?
- 如果通过分页导出,每次点击按钮只导2万条,分批导出难道不能满足业务需求吗?
如果产品说 “甲方是爸爸,你去和甲方说啊”,“客户说这个做出来,才考虑付尾款!”,如果客户的确缺根筋要让你这样搞, 那就只能从技术上考虑如何实现了。
从技术上讲,为了避免OOM,我们一定要注意一个原则:
不能将全量数据一次性加载到内存之中。
全量加载不可行,那我们的目标就是如何实现数据的分批加载了。实事上,Mysql本身支持Stream查询,我们可以通过Stream流获取数据,然后将数据逐条刷入到文件中,每次刷入文件后再从内存中移除这条数据,从而避免OOM。
由于采用了数据逐条刷入文件,而且数据量达到百万级,所以文件格式就不要采用excel了,excel2007最大才支持104万行的数据。这里推荐:
以csv代替excel。
考虑到当前SpringBoot持久层框架通常为JPA和mybatis,我们可以分别从这两个框架实现百万级数据导出的方案。
JPA实现百万级数据导出
- 具体方案不妨参考:http://knes1.github.io/blog/2015/2015-10-19-streaming-mysql-results-using-java8-streams-and-spring-data.html。
实现项目对应:
- https://github.com/knes1/todo
核心注解如下,需要加入到具体的Repository之上。方法的返回类型定义成Stream。Integer.MIN_VALUE告诉jdbc driver逐条返回数据。
@QueryHints(value = @QueryHint(name = HINT_FETCH_SIZE, value = "" + Integer.MIN_VALUE))
@Query(value = "select t from Todo t")
Stream streamAll();
此外还需要在Stream处理数据的方法之上添加@Transactional(readOnly = true),保证事物是只读的。
同时需要注入javax.persistence.EntityManager,通过detach从内存中移除已经使用后的对象。
@RequestMapping(value = "/todos.csv", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public void exportTodosCSV(HttpServletResponse response) {
response.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/csv");
response.addHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=todos.csv");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
try(Stream todoStream = todoRepository.streamAll()) {
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
todoStream.forEach(rethrowConsumer(todo -> {
String line = todoToCSV(todo);
out.write(line);
out.write("\n");
entityManager.detach(todo);
}));
out.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.info("Exception occurred " + e.getMessage(), e);
throw new RuntimeException("Exception occurred while exporting results", e);
}
}
MyBatis实现百万级数据导出
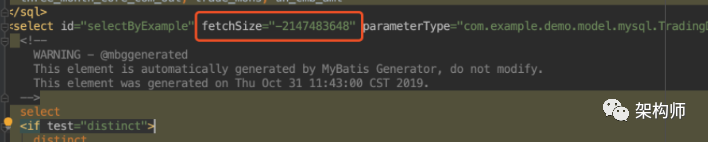
MyBatis实现逐条获取数据,必须要自定义ResultHandler,然后在mapper.xml文件中,对应的select语句中添加fetchSize="-2147483648"。
最后将自定义的ResultHandler传给SqlSession来执行查询,并将返回的结果进行处理。
MyBatis实现百万级数据导出的具体实例
以下是基于MyBatis Stream导出的完整的工程样例,我们将通过对比Stream文件导出和传统方式导出的内存占用率的差异,来验证Stream文件导出的有效性。
我们先定义一个工具类DownloadProcessor,它内部封装一个HttpServletResponse对象,用来将对象写入到csv。
public class DownloadProcessor {
private final HttpServletResponse response;
public DownloadProcessor(HttpServletResponse response) {
this.response = response;
String fileName = System.currentTimeMillis() + ".csv";
this.response.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/csv");
this.response.addHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename="+fileName);
this.response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
}
public void processData(E record) {
try {
response.getWriter().write(record.toString()); //如果是要写入csv,需要重写toString,属性通过","分割
response.getWriter().write("\n");
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
然后通过实现org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler,自定义我们的ResultHandler,它用于获取java对象,然后传递给上面的DownloadProcessor处理类进行写文件操作:
public class CustomResultHandler implements ResultHandler {
private final DownloadProcessor downloadProcessor;
public CustomResultHandler(
DownloadProcessor downloadProcessor) {
super();
this.downloadProcessor = downloadProcessor;
}
@Override
public void handleResult(ResultContext resultContext) {
Authors authors = (Authors)resultContext.getResultObject();
downloadProcessor.processData(authors);
}
}
实体类:
public class Authors {
private Integer id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private Date birthdate;
private Date added;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName == null ? null : firstName.trim();
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void
setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName == null ? null : lastName.trim();
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email == null ? null : email.trim();
}
public Date getBirthdate() {
return birthdate;
}
public void setBirthdate(Date birthdate) {
this.birthdate = birthdate;
}
public Date getAdded() {
return added;
}
public void setAdded(Date added) {
this.added = added;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.id + "," + this.firstName + "," + this.lastName + "," + this.email + "," + this.birthdate + "," + this.added;
}
}
Mapper接口:
public interface AuthorsMapper {
List selectByExample(AuthorsExample example);
List streamByExample(AuthorsExample example); //以stream形式从mysql获取数据
}
Mapper xml文件核心片段,以下两条select的唯一差异就是在stream获取数据的方式中多了一条属性:fetchSize="-2147483648"
<select id="selectByExample" parameterType="com.alphathur.mysqlstreamingexport.domain.AuthorsExample" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<if test="distinct">
distinct
if>
'false' as QUERYID,
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from authors
<if test="_parameter != null">
<include refid="Example_Where_Clause" />
if>
<if test="orderByClause != null">
order by ${orderByClause}
if>
select>
<select id="streamByExample" fetchSize="-2147483648" parameterType="com.alphathur.mysqlstreamingexport.domain.AuthorsExample" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<if test="distinct">
distinct
if>
'false' as QUERYID,
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from authors
<if test="_parameter != null">
<include refid="Example_Where_Clause" />
if>
<if test="orderByClause != null">
order by ${orderByClause}
if>
select>
获取数据的核心service如下,由于只做个简单演示,就懒得写成接口了。其中streamDownload方法即为stream取数据写文件的实现,它将以很低的内存占用从MySQL获取数据;此外还提供traditionDownload方法,它是一种传统的下载方式,批量获取全部数据,然后将每个对象写入文件。
@Service
public class AuthorsService {
private final SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate;
private final AuthorsMapper authorsMapper;
public AuthorsService(SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate, AuthorsMapper authorsMapper) {
this.sqlSessionTemplate = sqlSessionTemplate;
this.authorsMapper = authorsMapper;
}
/**
* stream读数据写文件方式
* @param httpServletResponse
* @throws IOException
*/
public void streamDownload(HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse)
throws IOException {
AuthorsExample authorsExample = new AuthorsExample();
authorsExample.createCriteria();
HashMap param = new HashMap<>();
param.put("oredCriteria", authorsExample.getOredCriteria());
param.put("orderByClause", authorsExample.getOrderByClause());
CustomResultHandler customResultHandler = new CustomResultHandler(new DownloadProcessor (httpServletResponse));
sqlSessionTemplate.select(
"com.alphathur.mysqlstreamingexport.mapper.AuthorsMapper.streamByExample", param, customResultHandler);
httpServletResponse.getWriter().flush();
httpServletResponse.getWriter().close();
}
/**
* 传统下载方式
* @param httpServletResponse
* @throws IOException
*/
public void traditionDownload(HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse)
throws IOException {
AuthorsExample authorsExample = new AuthorsExample();
authorsExample.createCriteria();
List authors = authorsMapper.selectByExample (authorsExample);
DownloadProcessor downloadProcessor = new DownloadProcessor (httpServletResponse);
authors.forEach (downloadProcessor::processData);
httpServletResponse.getWriter().flush();
httpServletResponse.getWriter().close();
}
}
下载的入口controller:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("download")
public class HelloController {
private final AuthorsService authorsService;
public HelloController(AuthorsService authorsService) {
this.authorsService = authorsService;
}
@GetMapping("streamDownload")
public void streamDownload(HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException {
authorsService.streamDownload(response);
}
@GetMapping("traditionDownload")
public void traditionDownload(HttpServletResponse response)
throws IOException {
authorsService.traditionDownload (response);
}
}
实体类对应的表结构创建语句:
CREATE TABLE `authors` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`first_name` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`last_name` varchar(50
) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`birthdate` date NOT NULL,
`added` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=10095 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci;
这里有个问题:如何短时间内创建大批量测试数据到MySQL呢?一种方式是使用存储过程 + 大杀器 select insert 语句!不太懂?
没关系,且看我另一篇文章 MySQL如何生成大批量测试数据 你就会明白了。如果你懒得看,我这里已经将生成的270多万条测试数据上传到网盘,你直接下载然后通过navicat导入就好了。
- 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1hqnWU2JKlL4Tb9nWtJl4sw
有了测试数据,我们就可以直接测试了。先启动项目,然后打开jdk bin目录下的jconsole.exe
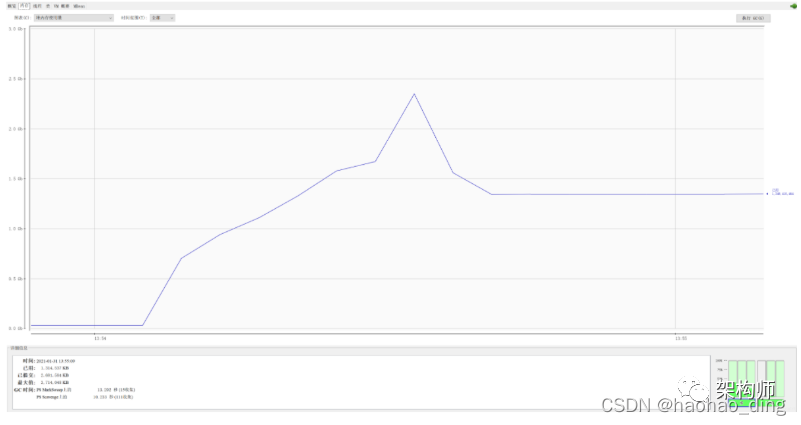
首先我们测试传统方式下载文件的内存占用,直接浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080/download/traditionDownload。
可以看出,下载开始前内存占用大概为几十M,下载开始后内存占用急速上升,峰值达到接近2.5G,即使是下载完成,堆内存也维持一个较高的占用,这实在是太可怕了,如果生产环境敢这么搞,不出意外肯定内存溢出。
接着我们测试stream方式文件下载的内存占用,浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080/download/streamDownload,当下载开始后,内存占用也会有一个明显的上升,但是峰值才到500M。对比于上面的方式,内存占用率足足降低了80%!怎么样,兴奋了吗!
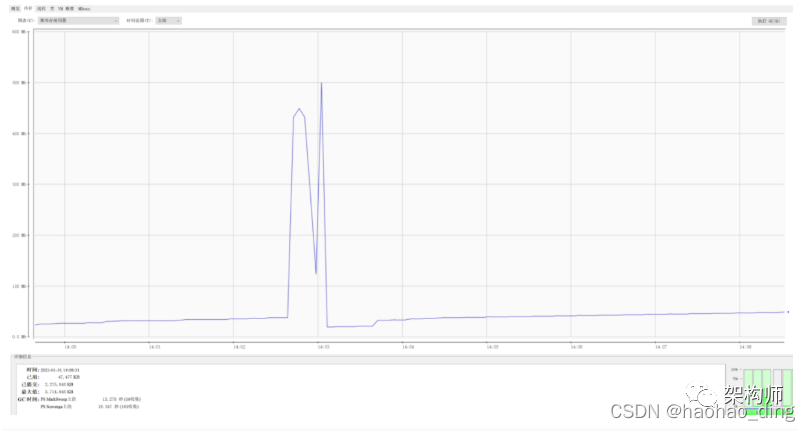
我们再通过记事本打开下载后的两个文件,发现内容没有缺斤少两,都是2727127行,完美!