来源:程序员书库(ID:OpenSourceTop)
如今的大型企业都在经历着自工业化以来最大的变革。人工智能颠覆了工业,颠覆了我们的工作、思考和互动的方式,Gartner的一项报告预测,到2020年,人工智能将创造230万个就业岗位,以此同时也会减少180万个人力岗位。机器学习是驱动人工智能发展的主要动力,这个领域的专家数量不多,各大企业都在争抢高技能人才。
说到这里,你可能已经猜到猿哥今天要和大家分享的是一本有关人工智能的书,这本书只有152页,非常简短。名叫——《The Hundred-Page Machine Learning Book》

但麻雀虽小五脏俱全,这本书涵盖了监督和非监督式学习,支持向量机,神经网络,集成方法,梯度下降法,聚类分析和数据降维,自编码和迁移学习,特征工程和超参数优化,数学知识、插图等内容都包含在这本152页的书籍里
具体的章节目录如下:
前言
第一部分:监督式学习
第二章:标记和定义
第三章:基础算法
第四章:学习算法的解剖
第五章:基础实战
第六章:神经网络与深度学习
第七章:问题与解决
第八章:进阶实战
第二部分:非监督式学习和其它学习
第九章:非监督式学习
第十章:其它形式学习
第十一章:结论
作者本着先阅读后购买的原则,因此你可以先在在线免费阅读/下载书籍,直到你认为它值得你购买的时候再购买。

这本书在线阅读还有一个好处就是,在页面的右侧有网友评论,你可以通过网友评论发现本书错误或者不足的地方,从而避免被误导,还能查看作者最新的更新时间等
除此之外,作者还在GitHub上开源了本书配套的所有代码
GitHub地址:https://github.com/aburkov/theMLbook
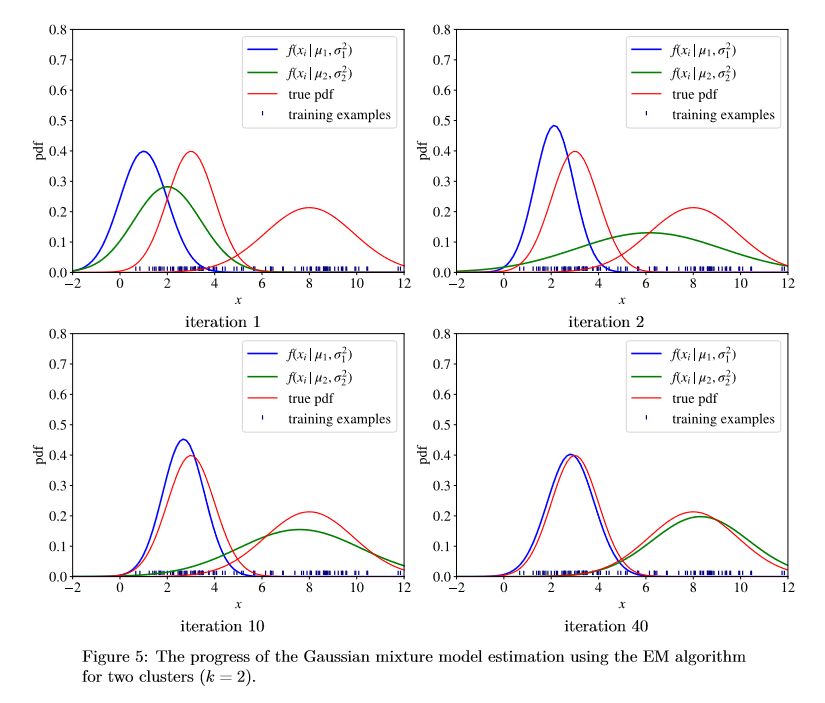
比如多元高斯分布(GaussianMixture Model GMM)这个内容,作者在书的9.2.4进行了详细的讲解:
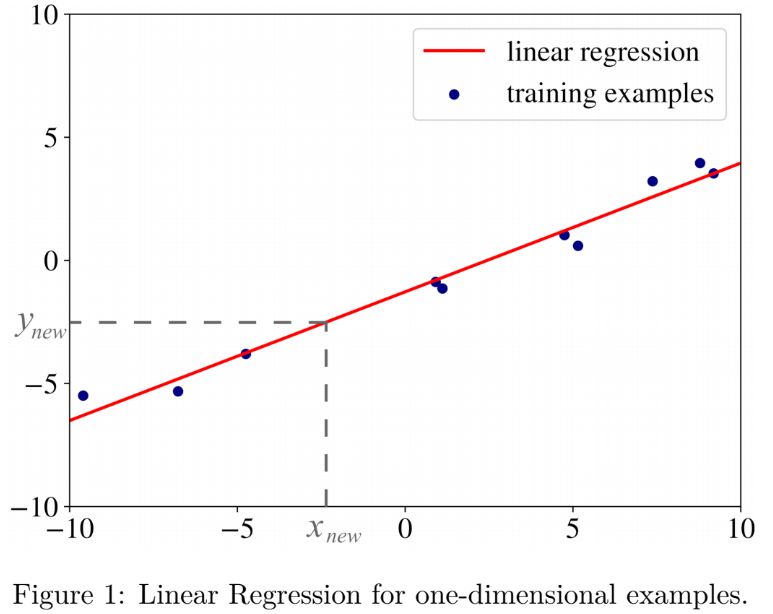
再如第三章中的关于线性回归算法的介绍:线性回归算法是一种流行的回归学习算法,学习的模型是利用数理统计中的回归分析
其对应的Python代码如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
import matplotlib
matplotlib.rcParams['mathtext.fontset'] = 'stix'
matplotlib.rcParams['font.family'] = 'STIXGeneral'
matplotlib.rcParams.update({'font.size': 18})
def f(x):
""" function to approximate by polynomial interpolation"""
return 0.5 * x
x_plot = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
rng.shuffle(x)
x = np.sort(x[:10])
noize = [(-2 + np.random.random()*2) for i in range(len(x))]
y = f(x) + noize
X = x[:, np.newaxis]
X_plot = x_plot[:, np.newaxis]
colors = ['red', 'red']
lw = 2
type_of_regression = ["linear regression", "regression of degree 10"]
fit = ["fit", "overfit"]
for count, degree in enumerate([1,10]):
plt.figure(count)
axes = plt.gca()
axes.set_xlim([-10,10])
axes.set_ylim([-10,10])
plt.scatter(x, y, color='navy', s=30, marker='o', label="training examples")
plt.xticks([-10.0, -5.0, 0.0, 5.0, 10.0])
plt.yticks([-10.0, -5.0, 0.0, 5.0, 10.0])
model = make_pipeline(PolynomialFeatures(degree), Ridge())
model.fit(X, y)
y_plot = model.predict(X_plot)
plt.plot(x_plot, y_plot, color=colors[count], linewidth=lw,
label=type_of_regression[count])
plt.legend(loc='best')
fig1 = plt.gcf()
fig1.subplots_adjust(top = 0.98, bottom = 0.1, right = 0.98, left = 0.08, hspace = 0, wspace = 0)
fig1.savefig('../../Illustrations/linear-regression-' + fit[count] + '.eps', format='eps', dpi=1000, bbox_inches = 'tight', pad_inches = 0)
fig1.savefig('../../Illustrations/linear-regression-' + fit[count] + '.pdf', format='pdf', dpi=1000, bbox_inches = 'tight', pad_inches = 0)
fig1.savefig('../../Illustrations/linear-regression-' + fit[count] + '.png', dpi=1000, bbox_inches = 'tight', pad_inches = 0)
plt.show()
也就是说这本书里的插图都附有源代码,这些源代码你都可以在GitHub上找到。
关于作者

Andriy Burkov,是一名机器学习专家,早在九年前就已经取得了博士学位,他的专长是自然语言处理,在人工智能方面,过去的7年里,Andriy Burkov一直在Gartner带领一个机器学习开发团队。
最后,附上本书的下载地址:
http://themlbook.com/wiki/doku.php
●编号661,输入编号直达本文
●输入m获取到文章目录
