海归学者发起的公益学术平台
分享信息,整合资源
交流学术,偶尔风月

预测具有超高热导率的新材料一直是学术界和工业界的研究热点,但由于基于第一性热导率计算的低效率以及广域材料空间极小值点搜索的复杂性,迄今只有极少数晶体被证实具有超过800 W m−1 K−1的超高热导率。机器学习技术的发展为加速新材料开发提供了全新途径:一方面,机器学习势函数通过加速原子相互作用预测实现了高效的热物性计算,但在预测未知材料的结构和热物性时可能会出现显著误差;另一方面,生成式模型通过材料空间的联合概率分布学习与直接采样重建,可实现材料空间快速的广域搜索,但因缺乏严格的物理约束,在寻找具有动力学稳定性的材料方面仍面临显著挑战。
发展为加速新材料开发提供了全新途径:一方面,机器学习势函数通过加速原子相互作用预测实现了高效的热物性计算,但在预测未知材料的结构和热物性时可能会出现显著误差;另一方面,生成式模型通过材料空间的联合概率分布学习与直接采样重建,可实现材料空间快速的广域搜索,但因缺乏严格的物理约束,在寻找具有动力学稳定性的材料方面仍面临显著挑战。
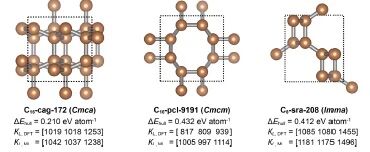
来自清华大学航天航空学院的曹炳阳教授和来自加州大学戴维斯分校的Davide Donadio教授团队,提出了一种融合晶体结构生成模型与机器学习势函数的超高热导率材料预测方法框架。该研究通过系统性量化生成模型输出结构与其能量最优构型间的几何偏差,揭示近半数生成结构存在显著晶格应变(> 10%)与畸变(> 7%)。鉴于晶格热导率对原子尺度结构扰动的高敏感性,这一发现突显了基于物理约束的生成空间优化的必要性。此外,该研究还引入结构对称性度量过滤低对称及复杂结构,并通过基于原子局域环境的相似性指标优先选择与已知高导热材料具有几何相似性的候选结构,大幅提升了计算效率。该框架展现出先验知识非依赖性优势,在近乎零标注数据的条件下优于其他逆向设计过程。团队将该框架应用于碳材料体系研究,成功地从生成模型产生的100,000个候选结构识别出34种突破800 W m−1 K−1的超高导热相,包括5种已知材料(如金刚石)与8种完全新型的高导热结构,其余21种结构的超高导热性质则首次被报道,其中非金刚石相的最高热导率超过2,400 W m−1 K−1。
Fig. 1 | The overview of our approach.
Fig. 2 | Performance evaluation of the generative model.
Fig. 3 | Machine learning-driven exploration of ultrahigh κL materials.
该框架支持向多元组分体系的拓展,结合通用型高精度机器学习势函数的持续发展,有望为新型功能材料设计建立新范式。该文近期发表于npj Computational Materials 11, 97 (2025),英文标题与摘要如下,点击左下角“阅读原文”可以自由获取论文PDF。
Generative deep learning for predicting ultrahigh lattice thermal conductivity materials
Liben Guo, Yuanbin Liu, Zekun Chen, Hongao Yang, Davide Donadio & Bingyang Cao
Developing materials with ultrahigh thermal conductivity is crucial for thermal management and energy conversion. The recent development of generative models and machine learning (ML) holds great promise for predicting new functional materials. However, these data-driven methods are not tailored to identifying energetically stable structures and accurately predicting their thermal properties, as they lack physical constraints and information about the complexity of atomic many-body interactions. Here, we show how combining deep generative models of crystal structures with quantum-accurate, fast ML interatomic potentials can accelerate the prediction of materials with ultrahigh lattice thermal conductivity while ensuring energy optimality. We exploit structural symmetry and similarity metrics derived from atomic coordination environments to enable fast exploration of the structural space produced by the generative model. Additionally, we propose an active-learning-based protocol for the on-the-fly training of ML potentials to achieve high-fidelity predictions of stability and lattice thermal conductivity in prospective materials. Applying this method to carbon materials, we screen 100,000 candidates and identify 34 carbon polymorphs, approximately a quarter of which had not been previously predicted, to have lattice thermal conductivity above 800 W m−1 K−1, reaching up to 2,400 W m−1 K−1 aside from diamond. These findings provide a viable pathway toward the ML-assisted prediction of periodic materials with exceptional thermal properties.