海归学者发起的公益学术平台
分享信息,整合资源
交流学术,偶尔风月

在原子级别的模拟中,研究者需要一个工具来描述原子之间是怎么“互相作用”的,这个工具就是原子间势函数。传统的势函数是基于物理理论和一些近似方法构建的。而如今,机器学习原子间势函数(MLIP)发展迅速,它靠数据驱动,拟合能力特别强,能应对各种复杂材料系统。
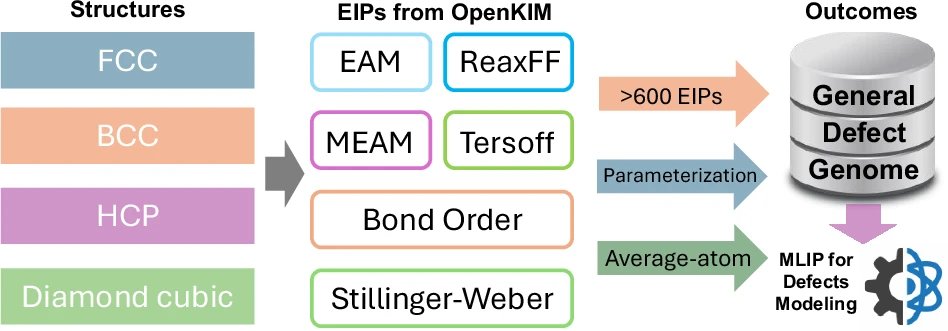
不过,MLIP的能力有多强,很大程度上取决于它“见过多少东西”——也就是它的训练数据集。如果数据集不够丰富,训练出来的势函数自然也就不够“靠谱”。在实际操作中,我们容易构造一些结构整齐、接近平衡的原子构型,放进数据集里;但对金属中非常关键的结构,比如位错网络和晶界,它们复杂又难建模,常常被忽略。
没有“缺陷”,就很难做出真正强大的势函数。以往的办法是“主动学习”——在模拟过程中实时监测那些势函数没见过的新环境,提取出来之后再做一遍昂贵的第一性原理(DFT)计算。这方法虽然有效,但效率不高,计算成本也不小。
来自荷兰代尔夫特理工大学的双飞博士团队提出了一种更聪明的解决方案。他们开发了一种由经典势函数引导的蒙特卡罗–分子动力学方法,可以高效、自动地重构包含缺陷的原子结构,从而大大简化了构建数据集的过程。这种方法可以用于各种类型的机器学习势函数,在钨(金属W)系统上的测试也显示出非常好的效果。
他们首先指出,以往常用的“球形原子簇”结构由于含有自由表面,计算结果容易偏离真实情况。于是他们利用经典的EAM势函数,引导蒙特卡罗方法对这些结构进行能量优化,最终得到的是能量更低、带周期性边界的结构。这些结构所包含的原子环境更加“真实”,也更适合用来训练势函数。相比之下,所需的计算量更小,效果却更好。
Fig. 1: The framework of versatile MLIP development for modeling extensive defects.
Fig. 2: Significance of PCC-GCMC in defect structure generation.
Fig. 3: Tensile deformation of BCC W polycrystals.
这个方法在钨系统的多种模拟任务中都表现出了出色的准确性,比如随机晶界、纳米压入、拉伸断裂等。最后,研究团队还提出了“缺陷基因组”的概念:借助大量现有的经典势函数,我们其实可以快速而系统地构建出金属中各种缺陷的训练集,从而加快MLIP的开发步伐。该文近期发表于npj Computational Materials 11::118 (2025),英文标题与摘要如下,点击左下角“阅读原文”可以自由获取论文PDF。
Modeling extensive defects in metals through classical potential-guided sampling and automated configuration reconstruction
Fei Shuang, Kai Liu, Yucheng Ji, Wei Gao, Luca Laurenti & Poulumi Dey
Extended defects such as dislocation networks and general grain boundaries are ubiquitous in metals, and accurate modeling these extensive defects is crucial to elucidate their deformation mechanisms. However, existing machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs) often fall short in adequately describing these defects, as their large characteristic scales exceed the computational limits of first-principles calculations. To address this challenge, we present a computational framework combining a defect genome constructed via empirical interatomic potential-guided sampling, with an automated reconstruction technique that enables accurate first-principles modeling of general defects by converting atomic clusters into periodic configurations. The effectiveness of this approach was validated through simulations of nanoindentation, tensile deformation, and fracture in BCC tungsten. This framework enhances the modeling accuracy of extended defects in crystalline materials and provides a robust foundation for advancing MLIP development by leveraging defect genomes strategically.