这段时间,笔者用c++写了一套机器人局部避障算法,并工程落地,机器人可以正常避障,避障所采用的技术方案是A*+TEB算法。并取得一定成果,后续还要针对复杂的场景继续优化。主要涉及到技术模块有:
(1) costmap:代价地图模块,分为静态层和障碍物层以及膨胀层,静态层将读取地图信息并根据机器人内切半径进行膨胀,障碍物层是根据搭载的传感器检测到的障碍物点云并且以机器人内切圆半径进行膨胀。
(2)全局规划器:这部分规划部分主要是A根据costmap规划一条路径。
(3)局部规划器(控制器):使用TEB去跟踪A生成的全局规划路径。同时具有局部避障能力。
(4)状态机:负责统筹costmap和全局规划器以局部规划器。
之前做过局部规划器的技术分享机器人控制算法——局部规划器TEB算法原理及C++可视化仿真。
本次就做全局规划器和静态代价地图的分享。
全局规划器
这个部分就是A*算法,网上很多教程。
C++实现
主函数如下:
#include#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include "../include/global_planner/astar.h"#include "../include/global_planner/expander.h"#include "../include/global_planner/traceback.h"#include "../include/global_planner/grid_path.h"#include "../include/global_planner/gradient_path.h"#include "../include/global_planner/quadratic_calculator.h"
struct point_cell{ int x; int y;};
costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS* planner_costmap_ros_;costmap_2d::Costmap2D* global_cost_map_; global_planner::QuadraticCalculator* p_calc_;global_planner::Expander* planner_;global_planner::Traceback* path_maker_;float* potential_array_;float convert_offset_;unsigned char* costs_; std::vector plan_result_cell_;
bool getPlanFromPotential(double start_x, double start_y, double goal_x, double goal_y, const point_cell goal,std::vector &plan){
plan.clear(); std::vector<std::pair<float, float> > path;
if (!path_maker_->getPath(potential_array_, start_x, start_y, goal_x, goal_y, path)) { std::cout << "NO PATH!" << std::endl; return false; }
for (int i = path.size() -1; i>=0; i--) { std::pair<float, float> point = path[i]; double world_x, world_y;
point_cell point_cell; point_cell.x = point.first; point_cell.y = point.second;
plan.push_back(point_cell); } plan.push_back(goal); return !plan.empty();}
bool makePlanner(point_cell start,point_cell goal,std::vector &plan){ plan.clear(); int nx = global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsX(), ny = global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsY();
p_calc_->setSize(nx, ny); planner_->setSize(nx, ny); path_maker_->setSize(nx, ny); potential_array_ = new float[nx * ny];
bool found_legal = planner_->calculatePotentials(global_cost_map_->getCharMap(),global_cost_map_,global_cost_map_,start.x, start.y, goal.x, goal.y, nx * ny * 2, potential_array_); if (found_legal) { if (getPlanFromPotential(start.x,start.y, goal.x, goal.y, goal, plan)) { point_cell goal_copy = goal; plan.push_back(goal_copy); } else { std::cout << "Failed to get a plan from potential when a legal potential was found. This shouldn't happen." << std::endl; } }else{ std::cout << "Failed to get a plan." << std::endl; } delete potential_array_; return !plan.empty();}
void show(){
{ cv::Mat m4 = cv::imread("/home/juchunyu/20231013/240308/costmap_2d_A_star/map/PM.pgm",cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE); cv::imshow("originalcharmap",m4); boost::unique_lock<:costmap2d:: class="code-snippet__keyword">mutex_t> lock_costmap(*(planner_costmap_ros_->getCostmap()->getMutex())); cv::Mat map_info(global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsY(), global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsX(), CV_8UC1);
cv::Mat map_info_temp(global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsY(), global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsX(), CV_8UC1); cv::Mat map_info_Rotate(global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsY(), global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsX(), CV_8UC1); for(int i = 0;i < (global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsX())*(global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsY());i++) { int x = i % global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsX(); int y = i / global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsX(); map_info_temp.at<unsigned char>(y, x) = 254 - costs_[i]; } std::cout << "plan_result_cell_.size = " << plan_result_cell_.size() << std::endl; for(int i = 0;i < plan_result_cell_.size();i++){ map_info_temp.at<unsigned char>(plan_result_cell_[i -1].y,plan_result_cell_[i-1].x) = 0; } for(int j = 0,k = global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsY();k > 0 && j < global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsX(); j++,k--){ for(int i = 0,l = 0;l < global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsX() && i < global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsX();i++,l++){ map_info.at<unsigned char>(j,i) = map_info_temp.at<unsigned char>(k, l); } }
cv::imshow("map_info_char_map", map_info); cv::waitKey(0.5); if (cv::waitKey(1) == 'q') { } } }
int main(){
planner_costmap_ros_ = new costmap_2d::Costmap2DROS("global_costmap");
boost::this_thread::sleep_for(boost::chrono::seconds(5)); global_cost_map_ = planner_costmap_ros_->getCostmap(); costs_ = global_cost_map_->getCharMap(); unsigned int cx = global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsX(), cy = global_cost_map_->getSizeInCellsY(); convert_offset_ = 0.5; p_calc_ = new global_planner::QuadraticCalculator(cx, cy);
planner_ = new global_planner::AStarExpansion(p_calc_, cx, cy);
bool use_grid_path; path_maker_ = new global_planner::GridPath(p_calc_); path_maker_->setLethalCost(costmap_2d::INSCRIBED_INFLATED_OBSTACLE);
point_cell start; point_cell goal;
double start_x =683; double start_y =cy - 933;
double goal_x = 1347; double goal_y = cy - 294; start.x = start_x; start.y = start_y; goal.x = goal_x; goal.y = goal_y;
std::cout << "start:" << start.x << " " << start.y << std::endl; std::cout << "goal:" << goal.x << " " << goal.y << std::endl; bool gotPlan = makePlanner(start,goal,plan_result_cell_);
for(int i = 0; i < plan_result_cell_.size();i++){ std::cout << plan_result_cell_[i].x << " " << plan_result_cell_[i].y << std::endl; }
show();
}
运行效果
cd buildcmake ..make -j3./costmap
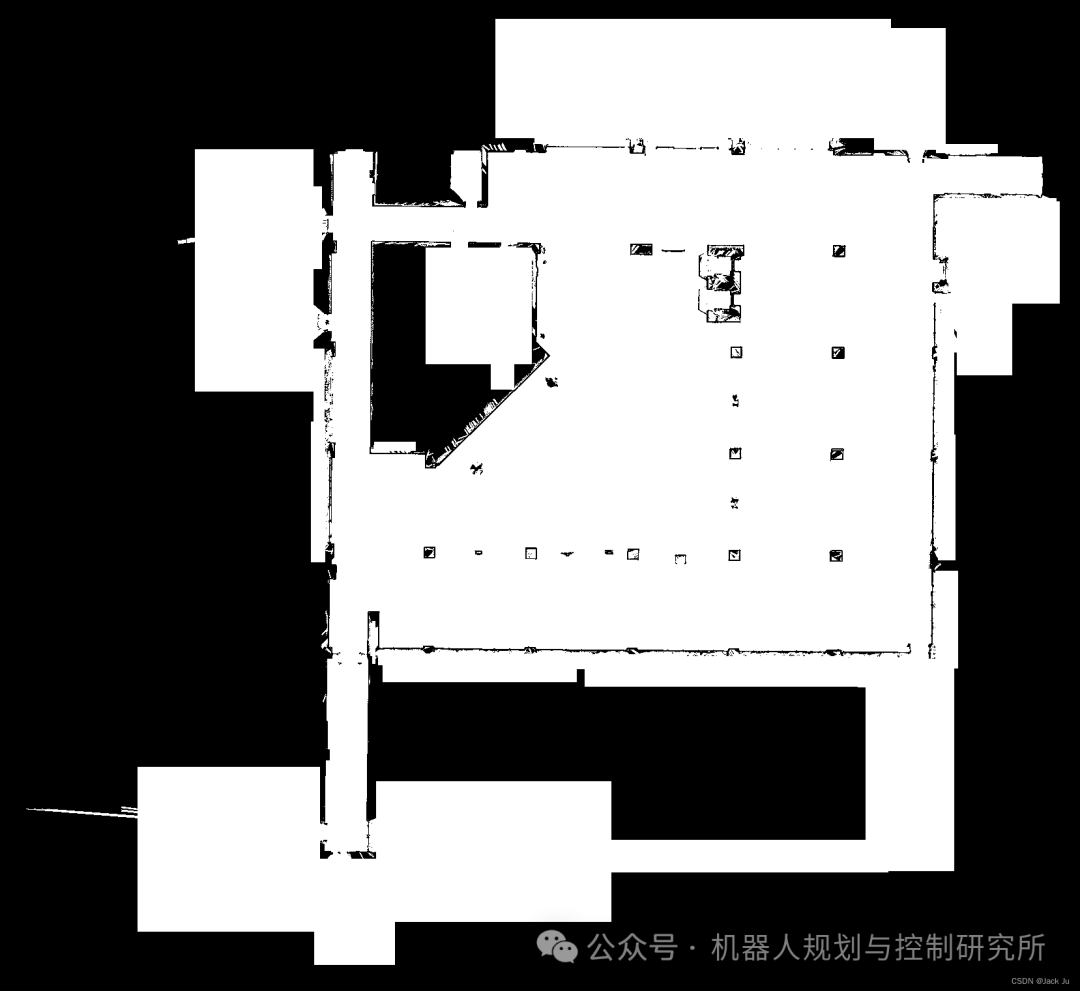
这是原始地图:
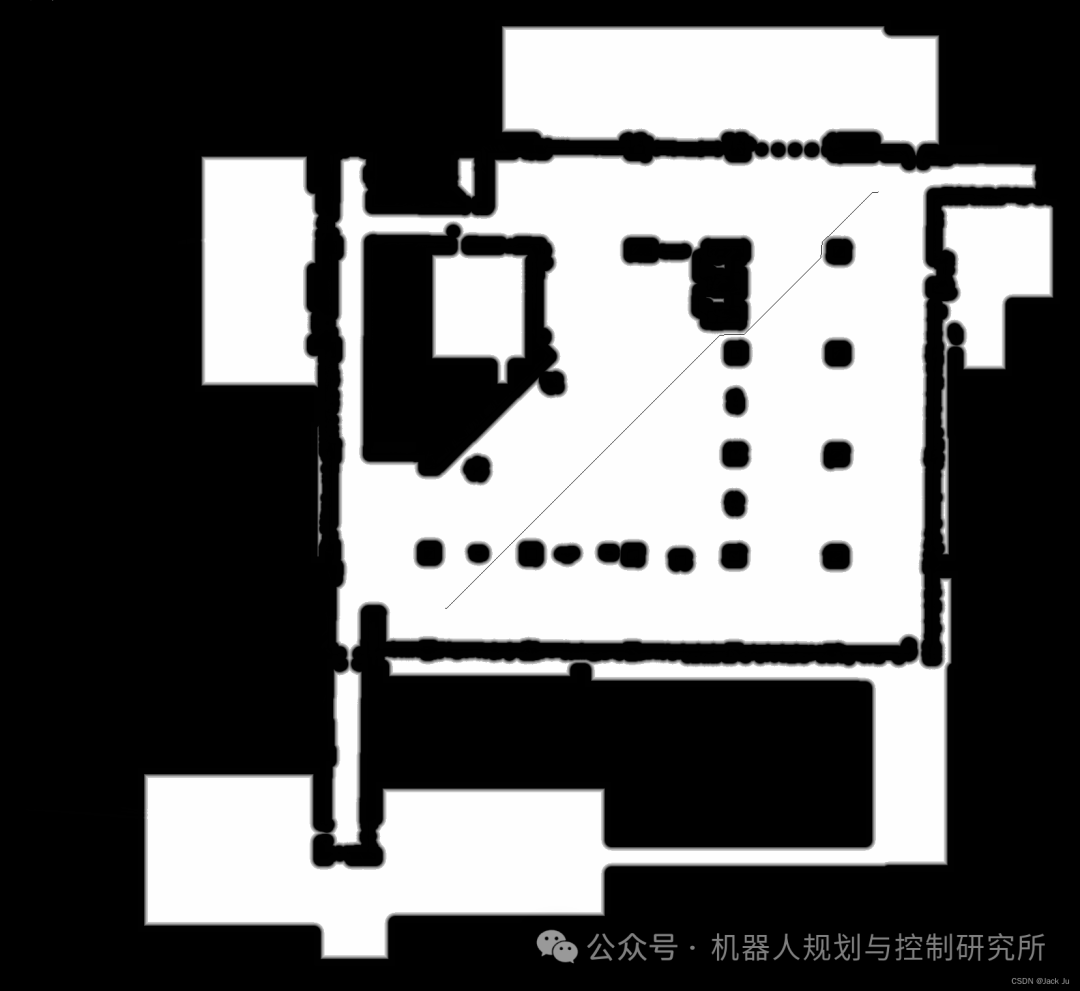
经过代价地图costmap处理后的膨胀地图(内切半径inscribed_radius_ = 0.5,膨胀半径inflation_radius_ =0.8)以及全局规划器生成的路径如图:
结论
本文主要不是解释基本的机器人算法的原理,适用于对代价地图和路径规划有一定了解的,重要的思想都在代码里,可以直接在ubuntu上直接运行,然后可以直接学习并在机器人上部署,完整代码请参照链接:global__plan_A-star(https://github.com/JackJu-HIT/global__plan_A-star)。