海归学者发起的公益学术平台
分享信息,整合资源
交流学术,偶尔风月

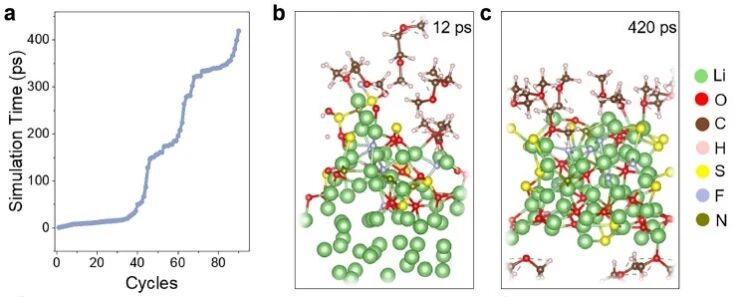
电极-电解质界面是决定电池性能的关键区域,它影响着锂离子传输、固体电解质界面 (SEI) 形成和整体循环稳定性等关键性能。然而,由于原位实时实验技术的时空限制和传统模拟方法的效率-精度限制,全面理解界面反应仍然具有挑战性。例如,元素掺杂通常用于提高锂离子电导率和界面稳定性。然而,元素掺杂后界面动态演化的普遍原理仍不清楚。虽然从头算分子动力学 (AIMD) 可以实现高精度模拟界面演化,但其高昂的计算成本限制了模拟的可及空间和时间尺度。机器学习势场使大规模模拟成为可能,但对于复杂界面环境中的动态变化,模拟常常存在分布偏移挑战。
来自北京大学新材料学院的郑家新团队,开发了一个混合AIMD和MLP的框架来模拟电极-电解质界面。HAML的创新在于它能够原位引导反应途径,耦合的 AIMD 能够引导MLP 走向物理相关的构型。这种架构使 HAML 能够实现界面反应的稳定、长时间尺度的模拟,解决了 MLP 在处理复杂界面构型时的分布偏移挑战。HAML 显著提高了效率并简化了仿真过程。他们应用该方法模拟锂金属与液态和固态电解质之间的界面反应,证明了其在长时间尺度上捕获关键反应过程和产物的高精度和高效性。对于电解液,HAML以高时空分辨率准确捕捉SEI 组分的动态演化。对于固态电解质,HAML揭示了相间层的形成和稳定,为了解其与锂金属的兼容性提供了见解。具体而言,针对氯化物固态电解质LPSC,他们引入了Se、F、O元素掺杂,以改变电解质与锂金属负极之间的界面结构和反应性。掺杂LPSC结构的内在不稳定性加速了界面反应动力学,促进了界面保护层的形成,从而提高了全电池系统的整体稳定性。结合以往的研究,界面处的表面稳定性存在各向异性,电解质分解行为在不同的晶体学方向上有所不同,不稳定的晶面处倾向于形成更稳定的保护层。因此,引入适度的晶格不稳定性可以作为调节界面反应动力学、产生稳定的SEI层和减轻进一步降解的有效策略。
图1. HAML方法的示意图
图2. HAML与AIMD在平均用时及加速比方面的比较
图3. 四种体系(Li|LPSC、Li|LPSC_Se、Li|LPSC_F 和 Li|LPSC_O)中界面反应的比较
这些发现不仅加深了对锂电池负极-电解质界面演化过程的理解,也为合理设计策略以增强下一代储能系统的稳定性和性能铺平了道路。该文近期发表于npj Computational Materials 11,245(2025),英文标题与摘要如下,点击左下角“阅读原文”可以自由获取论文PDF。
Machine-learning-accelerated mechanistic exploration of interface modification in lithium metal anode
Genming Lai, Ruiqi Zhang, Chi Fang, Juntao Zhao, Taowen Chen, Yunxing Zuo, Bo Xu & Jiaxin Zheng
Although the electrode-electrolyte interface is a crucial electrochemical region, the comprehensive understanding of interface reactions is limited by the time and space scales of experimental tools. Theoretical simulations with this delicate interface also remain one of the most significant challenges for atomistic modeling, particularly for the stable long-timescale simulation of the interface. Here we introduce a novel scheme, hybrid ab initio molecular dynamics combined with machine learning potential (HAML), to accelerate the modeling of electrode-electrolyte interface reactions. We demonstrate its effectiveness in modeling the interfaces of Li metal with both liquid and solid-state electrolytes, capturing critical processes over extended time scales. Furthermore, we reveal the role of interface reaction kinetics in interface regulation through HAML simulations, combined with the similarity analysis method. It is demonstrated that element (Se, F, O) doping in the Li6PS5Cl system is an effective strategy for enhancing interface reaction kinetics, facilitating the formation of a more stable interface protective layer faster at room temperature. Moreover, moderate structural instability can positively contribute to interface stabilization. HAML offers a promising approach for addressing the challenge of designing stable interfaces while reducing computational costs. This work provides valuable insights for advancing the understanding and optimization of interface behaviors in Li metal batteries.