基于大众对Python的大肆吹捧和赞赏,作为一名Java从业人员,看了Python的书籍之后,决定做一名python的脑残粉。
作为一名合格的脑残粉(标题党 (ノ◕ω◕)ノ),为了发展我的下线,接下来我会详细的介绍 Python 的安装 到开发工具的简单介绍,并编写一个抓取天气信息数据并存储到数据库的例子。(这篇文章适用于完全不了解Python的小白超超超快速入门)
源自:
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhaww/p/9517514.html#4049153
如果有时间的话,强烈建议跟着一起操作一遍,因为介绍的真的很详细了。
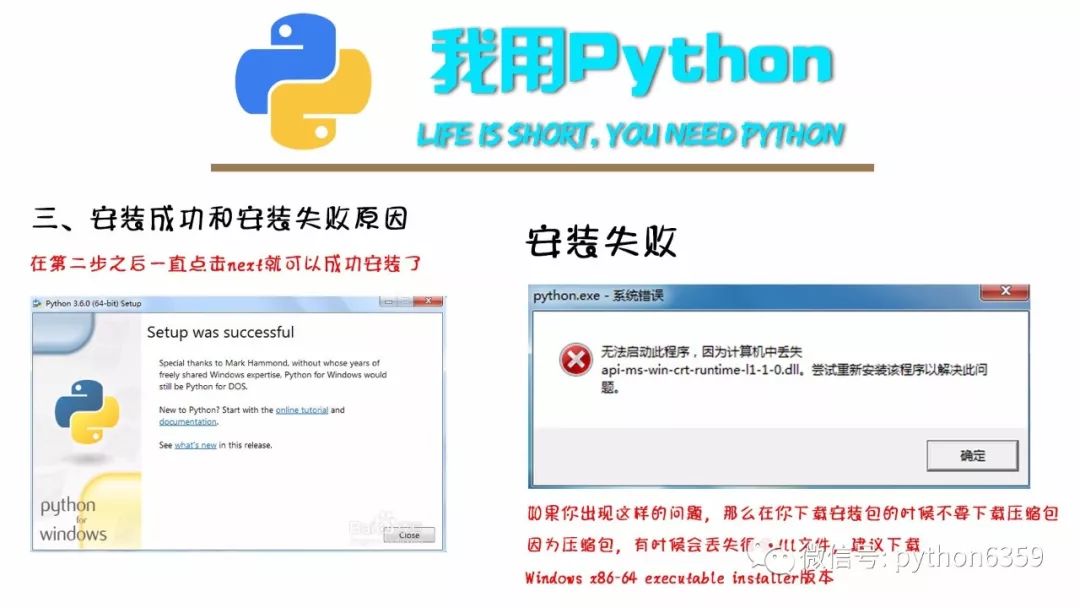
1、Python 安装
2、PyCharm(ide) 安装
3、抓取天气信息
4、数据写入excel
5、数据写入数据库
1、Python安装
下载 Python: 官网地址: https://www.python.org/ 选择download 再选择你电脑系统,小编是Windows系统的 所以就选择

2、Pycharm安装
下载 PyCharm : 官网地址:http://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/

免费版本的可以会有部分功能缺失,所以不推荐,所以这里我们选择下载企业版。
安装好 PyCharm,首次打开可能需要你 输入邮箱 或者 输入激活码
获取免费的激活码:http://idea.lanyus.com/
3、抓取天气信息
我们计划抓取的数据:杭州的天气信息,杭州天气 可以先看一下这个网站。
实现数据抓取的逻辑:使用python 请求 URL,会返回对应的 HTML 信息,我们解析 html,获得自己需要的数据。(很简单的逻辑)
第一步:创建 Python 文件
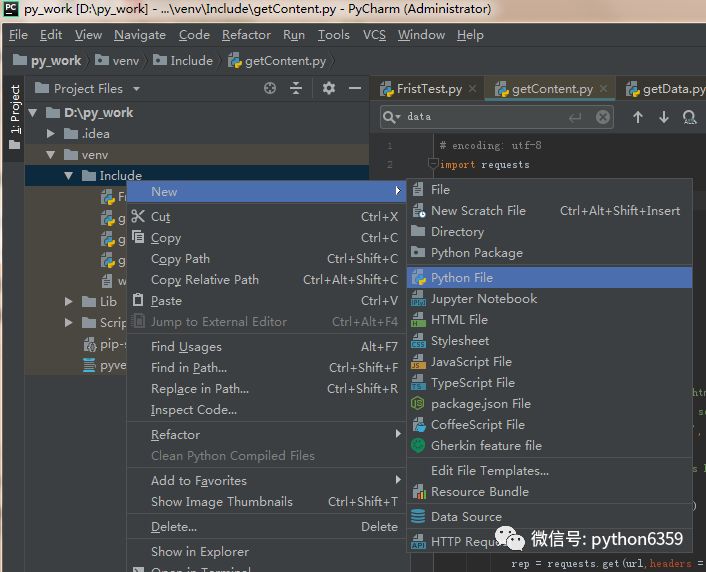
写第一段Python代码
if __name__ == '__main__':
url = 'http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101210101.shtml'
print('my frist python file')
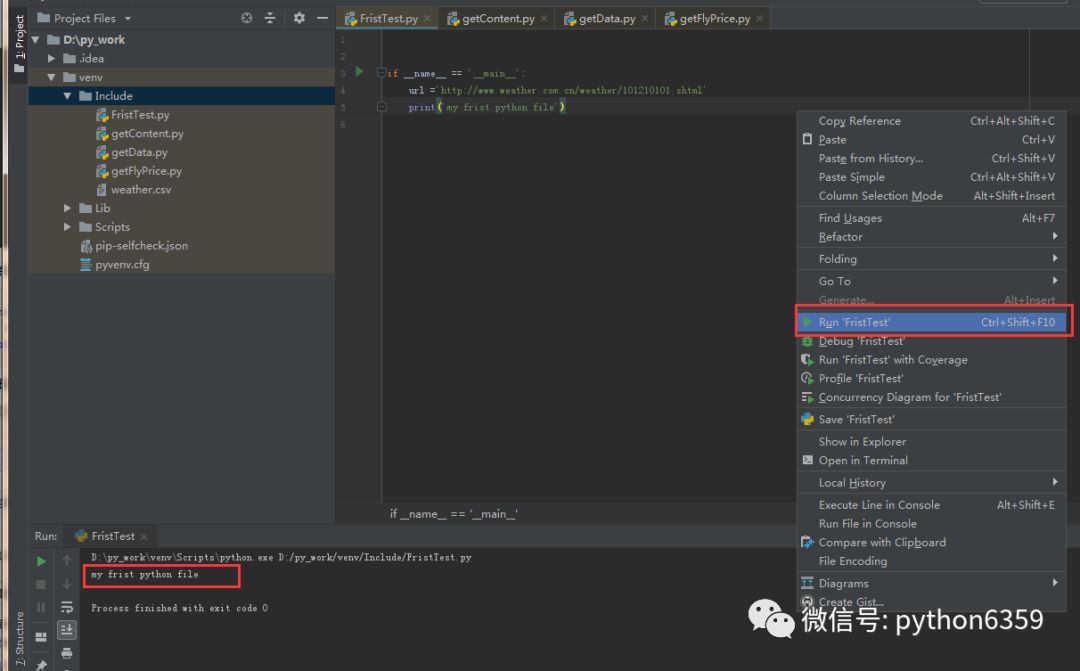
这段代码类似于 Java 中的 Main 方法。可以直接鼠标右键,选择 Run。
第二步:请求RUL
python 的强大之处就在于它有大量的模块(类似于Java 的 jar 包)可以直接拿来使用。
我们需要安装一个 request 模块: File - Setting - Product - Product Interpreter
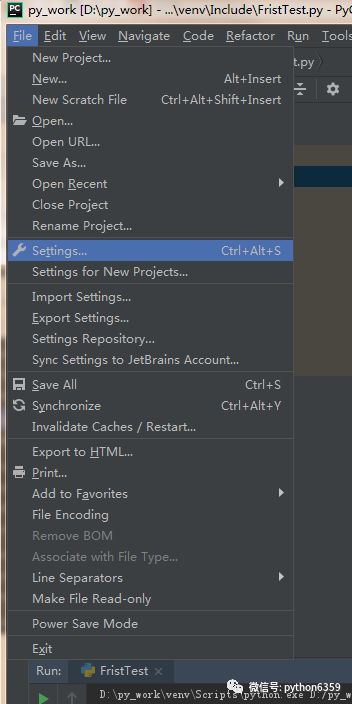
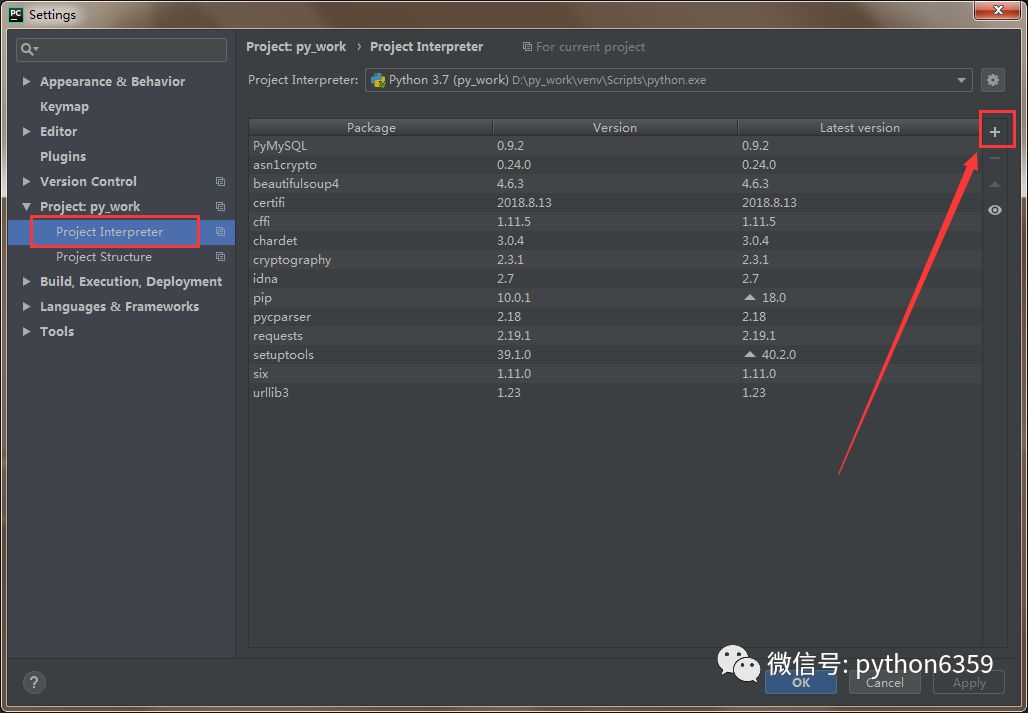
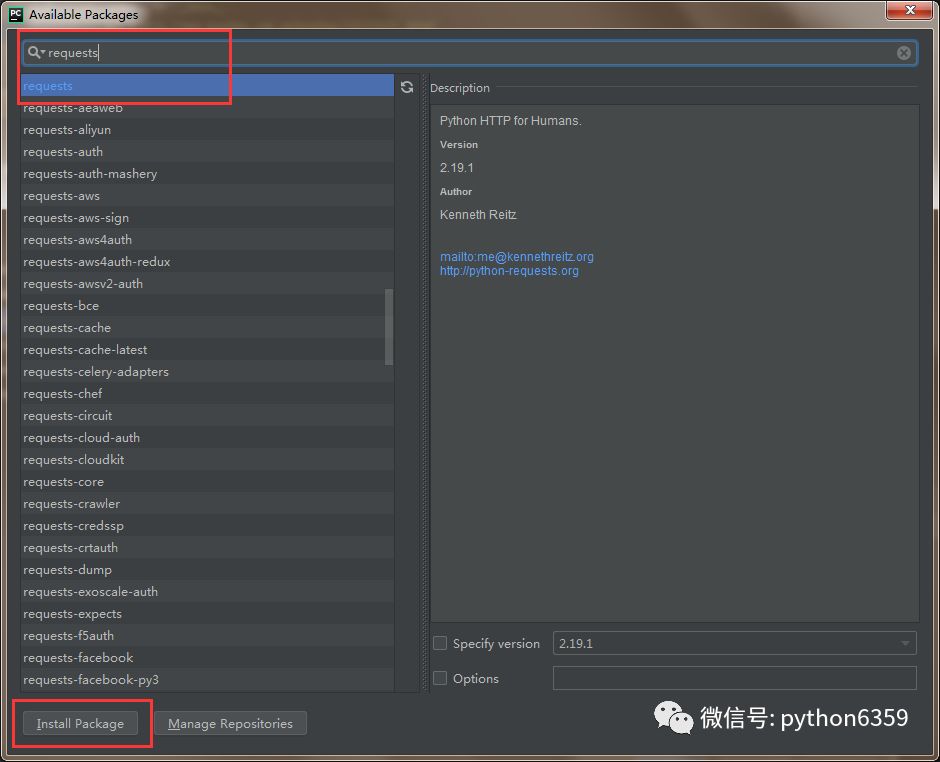
点击如上图的 + 号,就可以安装 Python 模块了。搜索 requests 模块(有 s 噢),点击 Install。
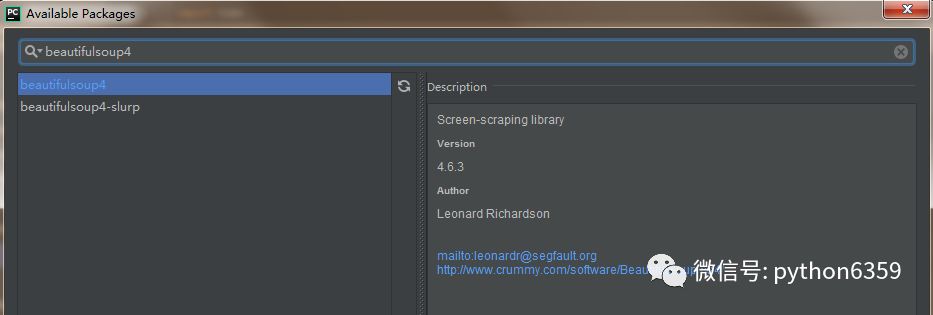
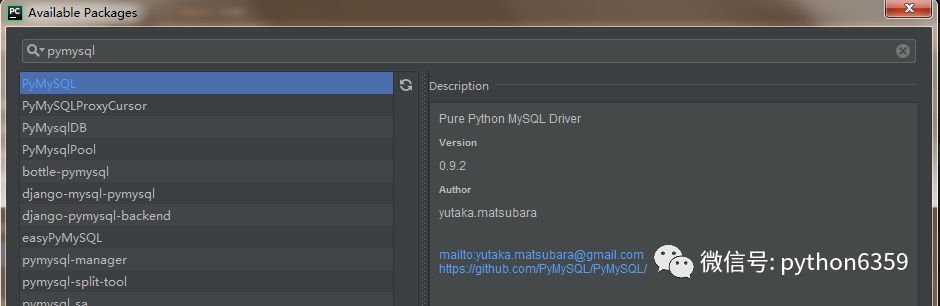
我们顺便再安装一个 beautifulSoup4 和 pymysql 模块,beautifulSoup4 模块是用来解析 html 的,可以对象化 HTML 字符串。pymysql 模块是用来连接 mysql 数据库使用的。
相关的模块都安装之后,就可以开心的敲代码了。
定义一个 getContent 方法:
import requests
import time
import random
import socket
import http.client
import pymysql
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
def getContent(url , data = None):
header={
'Accept':
'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8',
'Accept-Encoding': 'gzip, deflate, sdch',
'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.8',
'Connection': 'keep-alive',
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/43.0.235'
}
timeout = random.choice(range(80, 180))
while True:
try:
rep = requests.get(url,headers = header,timeout = timeout)
rep.encoding = 'utf-8'
break
except socket.timeout as e:
print( '3:', e)
time.sleep(random.choice(range(8,15)))
except socket.error as e:
print( '4:', e)
time.sleep(random.choice(range(20, 60)))
except http.client.BadStatusLine as e:
print( '5:', e)
time.sleep(random.choice(range(30, 80)))
except http.client.IncompleteRead as e:
print( '6:', e)
time.sleep(random.choice(range(5, 15)))
print('request success')
return rep.text
在 main 方法中调用:
if __name__ == '__main__':
url ='http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101210101.shtml'
html = getContent(url)
print('my frist python file')
第三步:分析页面数据
定义一个 getData 方法:
def getData(html_text):
final = []
bs = BeautifulSoup(html_text, "html.parser") # 创建BeautifulSoup对象
body = bs.body #获取body
data = body.find('div',{'id': '7d'})
ul = data.find('ul')
li = ul.find_all('li')
for day in li:
temp = []
date = day.find('h1').string
temp.append(date) #添加日期
inf = day.find_all('p')
weather = inf[0].string #天气
temp.append(weather)
temperature_highest = inf[1].find('span').string #最高温度
temperature_low = inf[1].find('i').string # 最低温度
temp.append(temperature_low)
temp.append(temperature_highest)
final.append(temp)
print('getDate success')
return final
上面的解析其实就是按照 HTML 的规则解析的。可以打开 杭州天气 在开发者模式中(F12),看一下页面的元素分布。
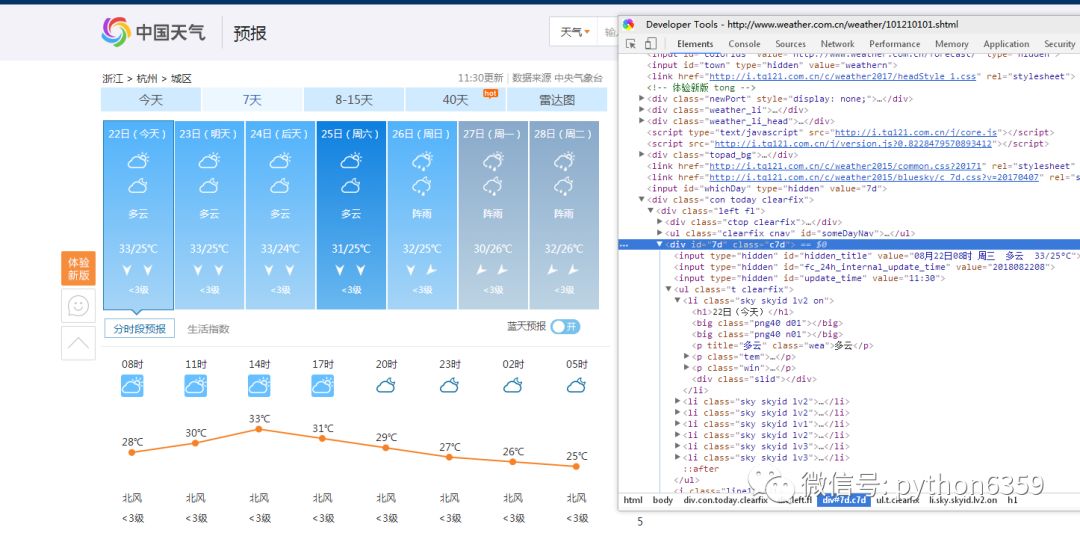
在 main 方法中调用:
if __name__ == '__main__':
url ='http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101210101.shtml'
html = getContent(url)
result = getData(html)
print('my frist python file')
数据写入excel
现在我们已经在 Python 中拿到了想要的数据,对于这些数据我们可以先存放起来,比如把数据写入 csv 中。
定义一个 writeDate 方法:
import csv
def writeData(data, name):
with open(name, 'a', errors='ignore', newline='') as f:
f_csv = csv.writer(f)
f_csv.writerows(data)
print('write_csv success')
在 main 方法中调用:
if __name__ == '__main__':
url ='http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101210101.shtml'
html = getContent(url)
result = getData(html)
writeData(result, 'D:/py_work/venv/Include/weather.csv')
print('my frist python file')
执行之后呢,再指定路径下就会多出一个 weather.csv 文件,可以打开看一下内容。
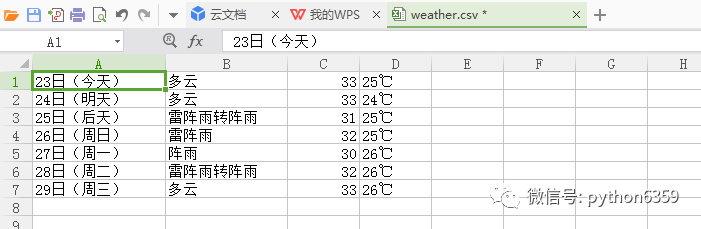
到这里最简单的数据抓取--储存就完成了。
数据写入数据库
因为一般情况下都会把数据存储在数据库中,所以我们以 mysql 数据库为例,尝试着把数据写入到我们的数据库中。
第一步创建WEATHER 表:
创建表可以在直接在 mysql 客户端进行操作,也可能用 python 创建表。在这里 我们使用 python 来创建一张 WEATHER 表。
定义一个 createTable 方法:(之前已经导入了 import pymysql 如果没有的话需要导入包)
def createTable():
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "zww", "960128", "test")
cursor = db.cursor()
cursor.execute("SELECT VERSION()")
data = cursor.fetchone()
print("Database version : %s " % data)
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS WEATHER")
sql = """CREATE TABLE WEATHER (
w_id int(8) not null primary key auto_increment,
w_date varchar(20) NOT NULL ,
w_detail varchar(30),
w_temperature_low varchar(10),
w_temperature_high varchar(10)) DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8"""
cursor.execute(sql)
db.close()
print('create table success')
在 main 方法中调用:
if __name__ == '__main__':
url ='http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101210101.shtml'
html = getContent(url)
result = getData(html)
writeData(result, 'D:/py_work/venv/Include/weather.csv')
createTable()
print('my frist python file')
执行之后去检查一下数据库,看一下 weather 表是否创建成功了。
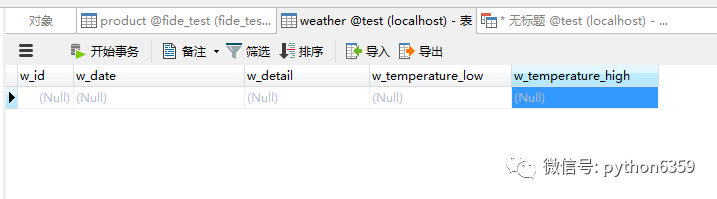
第二步批量写入数据至 WEATHER 表:
定义一个 insertData 方法:
def insert_data(datas):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "zww", "960128", "test")
cursor = db.cursor()
try:
cursor.executemany('insert into WEATHER(w_id, w_date, w_detail, w_temperature_low, w_temperature_high) value(null, %s,%s,%s,%s)', datas)
db.commit()
except Exception as e:
print('插入时发生异常' + e)
db.rollback()
db.close()
在 main 方法中调用:
if __name__ == '__main__':
url ='http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101210101.shtml'
html = getContent(url)
result = getData(html)
writeData(result, 'D:/py_work/venv/Include/weather.csv')
insertData(result)
print('my frist python file')
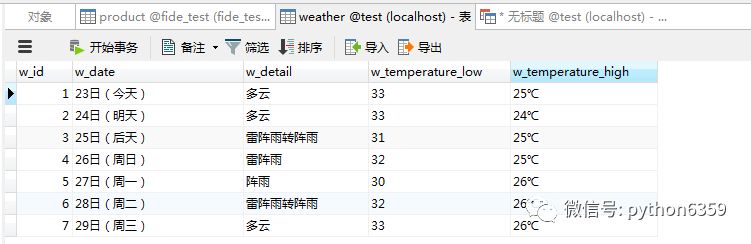
检查:执行这段 Python 语句后,看一下数据库是否有写入数据。有的话就大功告成了。
全部代码看这里:
import requests
import time
import random
import socket
import http.client
import pymysql
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import csv
def getContent(url , data = None):
header={
'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8',
'Accept-Encoding': 'gzip, deflate, sdch',
'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.8',
'Connection': 'keep-alive',
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/43.0.235'
}
timeout = random.choice(range(80, 180))
while True:
try:
rep = requests.get(url,headers = header,timeout = timeout)
rep.encoding = 'utf-8'
break
except socket.timeout as e:
print( '3:', e)
time.sleep(random.choice(range(8,15)))
except socket.error as e:
print( '4:', e)
time.sleep(random.choice(range(20, 60)))
except http.client.BadStatusLine as e:
print( '5:', e)
time.sleep(random.choice(range(30, 80)))
except http.client.IncompleteRead as e:
print( '6:', e)
time.sleep(random.choice(range(5, 15)))
print('request success')
return rep.text
def getData(html_text):
final = []
bs = BeautifulSoup(html_text, "html.parser")
body = bs.body
data = body.find('div',{'id': '7d'})
ul = data.find('ul')
li = ul.find_all('li')
for day in li:
temp = []
date = day.find('h1').string
temp.append(date)
inf = day.find_all('p')
weather = inf[0].string
temp.append(weather)
temperature_highest = inf[1].find('span').string
temperature_low = inf[1].find('i').string
temp.append(temperature_highest)
temp.append(temperature_low)
final.append(temp)
print('getDate success')
return final
def writeData(data, name):
with open(name, 'a', errors='ignore', newline='') as f:
f_csv = csv.writer(f)
f_csv.writerows(data)
print('write_csv success')
def createTable():
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "zww", "960128", "test")
cursor = db.cursor()
cursor.execute("SELECT VERSION()")
data = cursor.fetchone()
print("Database version : %s " % data)
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS WEATHER")
sql = """CREATE TABLE WEATHER (
w_id int(8) not null primary key auto_increment,
w_date varchar(20) NOT NULL ,
w_detail varchar(30),
w_temperature_low varchar(10),
w_temperature_high varchar(10)) DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8"""
cursor.execute(sql)
db.close()
print('create table success')
def insertData(datas):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "zww", "960128", "test")
cursor = db.cursor()
try:
cursor.executemany('insert into WEATHER(w_id, w_date, w_detail, w_temperature_low, w_temperature_high) value(null, %s,%s,%s,%s)', datas)
db.commit()
except Exception as e:
print('插入时发生异常' + e)
db.rollback()
db.close()
print('insert data success')
if __name__ == '__main__':
url ='http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101210101.shtml'
html = getContent(url)
result = getData(html)
writeData(result, 'D:/py_work/venv/Include/weather.csv')
insertData(result)
print('my frist python file')