本系列教程的目的,是帮助你学习怎样开发区块链技术。
在本教程中,我们将:
创建你的第一个基础“区块链” ;实现一个
简单的工作量证明(采矿) 系统;
(学习本教程之前,需要对面向对象编程有基本了解)
需要注意的是,本教程并没有生产区块链的完整功能。相反,这是一个概念实现的证明,以帮助您理解区块链,为以后的教程打基础。
教程中使用 Java,当然你可以使用其他的面向对象编程语言。 开发工具是 Eclipse,同样的你可以使用其他的文本编辑器(虽然你可能会错过很多好用的功能)。
你需要:
安装 Java 和 JDK;
Eclipse(或者其他 IDE/文本编辑器)。
你还可以使用谷歌发布的 GSON 类库,实现 Java 对象和 JSON 字符串之间的转换。这是个非常有用的类库,会在下文的点对点代码中继续使用,同样的,有其他方法能替换该类库。
在 Eclipse 中创建项目(文件>新建>) ,命名为“noobchain”。新建一个同名的类。
区块链即为一个由区块组成的链表或列表。其中的每个区块都包含自己的数字签名、前一区块的数字签名和一些数据(例如:事物)。
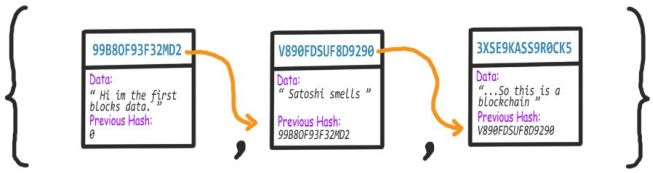
图中的 Hash(哈希) 即为数字签名。
每个区块不仅包含前一区块的哈希,还包含自己的哈希,根据前一区块的哈希计算得到。如果前一区块的数据变化,则其哈希也会变化(因为哈希的计算也与区块数据有关),继而影响其后面所有区块的哈希。计算和比较哈希可以检查区块链是否无效。
这意味着什么呢?这意味着如果改变了区块链中的任意数据,将改变签名并破坏区块链。
所以首先,创建类 Block 来构造区块链:
import java.util.Date;
public class Block {
public String hash;
public String previousHash;
private String data; //our data will be a simple message.
private long timeStamp; //as number of milliseconds since 1/1/1970.
//Block Constructor.
public Block(String data,String previousHash ) {
this.data = data;
this.previousHash = previousHash;
this.timeStamp = new Date().getTime();
}
}
可以看到 Block 类包含 String 类型的 hash 属性,用来表示数字签名。变量 previousHash表示前一区块的哈希,变量 data 表示区块数据。
接着需要一种方法来生成数字签名:
有 很 多 种 密 码 学 算 法 可 供 选 择 , 然 而 SHA256 算 法 最 为 适 合 。 导 入java.security.MessageDigest 来访问 SHA256 算法。
下文中还需要使用 SHA256 算法,所以创建一个 StringUtil 类并定义一个方法以方便使用:
import java.security.MessageDigest;
public class StringUtil {
//Applies Sha256 to a string and returns the result.
public static String applySha256(String input){
try {
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
//Applies sha256 to our input,
byte[] hash = digest.digest(input.getBytes("UTF-8"));
StringBuffer hexString = new StringBuffer(); // This will contain hash as
hexidecimal
for (int i = 0; i < hash.length; i++) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & hash[i]);
if(hex.length() == 1) hexString.append('0');
hexString.append(hex);
}
return hexString.toString();
}
catch(Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
如果你看不懂这个方法,不要担心,你只需要知道输入一个字符串,调用 SHA256 算法进行处理,将生成的签名作为字符串返回。
现在 Block 类中创建一个新方法,调用 applySha256 方法来计算哈希。必须使用所有不希望被篡改的区块中的哈希值进行计算,所以要用到变量
previousHash、 data 和 timeStamp(时间戳) 。
public String calculateHash() {
String calculatedhash = StringUtil.applySha256(
previousHash +
Long.toString(timeStamp) +
data
);
return calculatedhash;
}
将这些方法加到 Block 构造函数中:
public Block(String data,String previousHash ) {
this.data = data;
this.previousHash = previousHash;
this.timeStamp = new Date().getTime();
this.hash = calculateHash(); //Making sure we do this after we set the other
values.
}
是时候做一些测试了。
在 NoobChain 类中创建一些区块并输出其哈希到屏幕上,确保一切都运转正常。
第一个区块叫初始区块,因其前面没有区块,所以将 previousHash 的值设为 0。
public class NoobChain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Block genesisBlock = new Block("Hi im the first block", "0");
System.out.println("Hash for block 1 : " + genesisBlock.hash);
Block secondBlock = new Block("Yo im the second
block",genesisBlock.hash);
System.out.println("Hash for block 2 : " + secondBlock.hash);
Block thirdBlock = new Block("Hey im the third block",secondBlock.hash);
System.out.println("Hash for block 3 : " + thirdBlock.hash);
}
}
输出如下图所示:
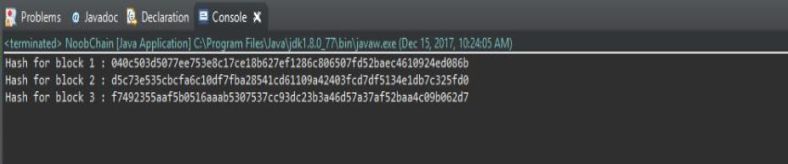
(你的哈希值会和图上不一样,因为我们的时间戳是不一样的)
这样, 每个区块都根据自己的信息和前一区块的签名,拥有了自己的数字签名。
目前还不是区块链,将所有区块保存为动态数组(ArrayList),并导入 gson 将其转化成 JSon 字符串来查看。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder;
public class NoobChain {
public static ArrayList blockchain = new ArrayList();
public static void main(String[] args) {
//add our blocks to the blockchain ArrayList:
blockchain.add(new Block("Hi im the first block", "0"));
blockchain.add(new Block("Yo im the second
block",blockchain.get(blockchain.size()-1).hash));
blockchain.add(new Block("Hey im the third
block",blockchain.get(blockchain.size()-1).hash));
String blockchainJson = new GsonBuilder().setPrettyPrinting().create().toJson(blockchain);
System.out.println(blockchainJson);
}
}
现在的输出看起来像我们期望的区块链了。
现在需要一种方法来验证区块链的完整性在 NoobChain 类中创建一个 isChainValid()方法,遍历链中所有区块并比较其哈希。该方法需要检查当前区块的哈希值是否等于计算得到的哈希值,以及前一区块的哈希是否等于当前区块 previousHash 变量的值。
public static Boolean isChainValid() {
Block currentBlock;
Block previousBlock;
//loop through blockchain to check hashes:
for(int i=1; i < blockchain.size(); i++) {
currentBlock = blockchain.get(i);
previousBlock = blockchain.get(i-1);
//compare registered hash and calculated hash:
if(!currentBlock.hash.equals(currentBlock.calculateHash()) ){
System.out.println("Current Hashes not equal");
return false;
}
//compare previous hash and registered previous hash
if(!previousBlock.hash.equals(currentBlock.previousHash) ) {
System.out.println("Previous Hashes not equal");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
链中区块发生任意的改变都会使该方法返回 false。
当人们将自己的区块链分享到比特币网络节点后,网络会接收其最长有效链。是什么阻止攻击者篡改旧区块上的数据,然后创建更长的新区块链并放在网络上呢? 工作量证明机制。哈希现金工作量证明机制意味着创建新的区块需要相当长的时间和计算能力。因此攻击者需要掌握巨大的计算能力,比其他所有同行加起来的计算能力还要多。
我们要让矿机完成工作量证明机制,即在区块中尝试不同的变量值,直到其哈希值以一定数量的 0 开始。
添加一个整数类型的 nonce 向量用于 calculateHash()方法中调用,并添加一个 mineBlock()方法:
import java.util.Date;
public class Block {
public String hash;
public String previousHash;
private String data; //our data will be a simple message.
private long timeStamp; //as number of milliseconds since 1/1/1970.
private int nonce;
//Block Constructor.
public Block(String data,String previousHash ) {
this.data = data;
this.previousHash = previousHash;
this.timeStamp = new Date().getTime();
this.hash = calculateHash(); //Making sure we do this after we set the other values.
}
//Calculate new hash based on blocks contents
public String calculateHash() {
String calculatedhash = StringUtil.applySha256(
previousHash +
Long.toString(timeStamp) +
Integer.toString(nonce) +
data
);
return calculatedhash;
}
public void mineBlock(int difficulty) {
String target = new String(new char[difficulty]).replace('\0', '0'); //Create a string with
difficulty * "0"
while(!hash.substring( 0, difficulty).equals(target)) {
nonce ++;
hash = calculateHash();
}
System.out.println("Block Mined!!! : " + hash);
}
}
实际上,每个矿机都从一个随机点开始迭代。有的矿机甚至可以尝试随机的数字。同样值得注意的是,在更困难的情况下可能需要的不仅仅是整数。 MAX_VALUE 的情况下,矿机可以尝试更改时间戳。
mineBlock()方法以整数变量 difficulty 作为输入,该变量(难度) 表示需要处理的 0 的数量。大多数计算机可以快速的处理 1 或 2 个 0 的情况,我建议在测试时处理 4 到 6 个 0。 莱特币的难度大约为 442592。
将 difficulty 作为一个静态变量添加到 NoobChain 类中:
public static int difficulty = 5;
我们需要更新 NoobChain 类来触发每个新区块的 mineBlock()方法。 同样需要 isChainValid()方法检查每个区块是否通过采矿得到了哈希值。
public class NoobChain {
public static ArrayList blockchain = new ArrayList();
public static int difficulty = 5;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//add our blocks to the blockchain ArrayList:
blockchain.add(new Block("Hi im the first block", "0"));
System.out.println("Trying to Mine block 1... ");
blockchain.get(0).mineBlock(difficulty);
blockchain.add(new Block("Yo im the second
block",blockchain.get(blockchain.size()-1).hash));
System.out.println("Trying to Mine block 2... ");
blockchain.get(1).mineBlock(difficulty);
blockchain.add(new Block("Hey im the third
block",blockchain.get(blockchain.size()-1).hash));
System.out.println("Trying to Mine block 3... ");
blockchain.get(2).mineBlock(difficulty);
System.out.println("\nBlockchain is Valid: " + isChainValid());
String blockchainJson = new GsonBuilder().setPrettyPrinting().create().toJson(blockchain);
System.out.println("\nThe block chain: ");
System.out.println(blockchainJson);
}
public static Boolean isChainValid() {
Block currentBlock;
Block previousBlock;
String hashTarget = new String(new char[difficulty]).replace('\0', '0');
//loop through blockchain to check hashes:
for(int i=1; i < blockchain.size(); i++) {
currentBlock = blockchain.get(i);
previousBlock = blockchain.get(i-1);
//compare registered hash and calculated hash:
if(!currentBlock.hash.equals(currentBlock.calculateHash()) ){
System.out.println("Current Hashes not equal");
return false;
}
//compare previous hash and registered previous hash
if(!previousBlock.hash.equals(currentBlock.previousHash) ) {
System.out.println("Previous Hashes not equal");
return false;
}
//check if hash is solved
if(!currentBlock.hash.substring( 0, difficulty).equals(hashTarget)) {
System.out.println("This block hasn't been mined");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
运行后的结果如图:
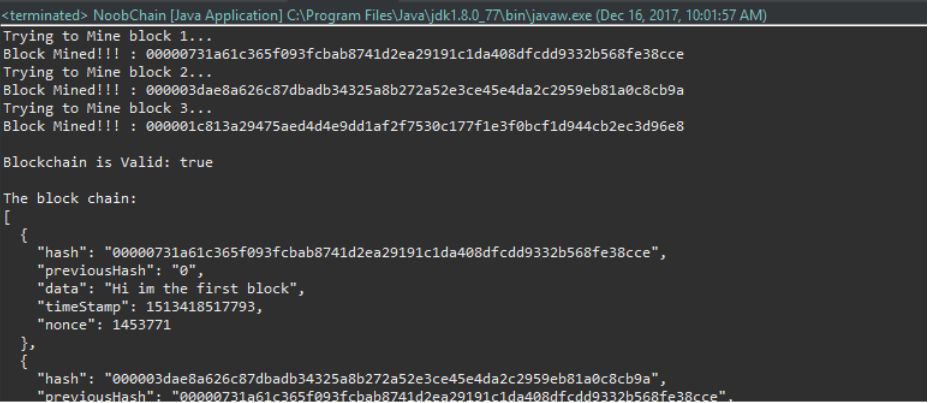
对每个区块采矿需要消耗一些时间(大约 3 秒) !测试中应该选取不同的难度值来观察对采矿时间的影响。
如果有人篡改了区块链中的数据:
一个被篡改的区块链将不可能赶上一个更长且有效的区块链。
除非他们的计算速度比你网络中所有节点的计算速度的总和还要快。 大概需要一台未来的量子计算机之类的。
恭喜你,你已经完成了你的基础区块链!
你的区块链:
由存储数据的区块构成。
有一个数字签名将区块链接起来。
需要工作量证明来验证新的区块。
可以验证数据是否有效且未被篡改。
下载项目文件:https://github.com/CryptoKass/NoobChain-Tutorial-Part-1
未完待续……
区块链领域常见术语
1) 区块链的工作量证明(POW): 一个将挖掘能力与计算能力联系起来的系统。块必须被散列,这本身就是一个简单的计算过程,但是在散列过程中增加了一个额外的变量,使其变得更加困难。当一个块被成功散列时,散列必须花费一些时间和计算量。因此,散列块被认为是工作量的证明。
2) 节点(Node): 连接到区块链网络的任何计算机
3) 挖掘(Mining): 验证交易并将其添加到区块链的过程
4) 莱特币(Litecoin): 基于 Scrypt 工作量证明网络的点对点加密货币。有时被称为比特币黄金中的白银。
5) 难度(Difficulty):在 POW 挖掘中,验证区块链网络中的区块是非常困难的。在比特币网络中,采矿难度调整为每隔 2016 个块进行验证,以保持块验证时间在十分钟。
6) 私钥(Private key): 一串数据,表明您可以访问特定钱包中的比特币。私钥可以被认为是一个密码, 私钥绝不能透露给任何人,因为密钥允许你通过加密签名从你的比特币钱包里支付比特币
7) 钱包(Wallet): 一个包含私钥集合的文件
本文由看雪论坛翻译小组 Green奇 编译,来源medium@kass
转载请注明来自看雪社区
往期热门阅读:
点击阅读原文/read,
更多干货等着你~

扫描二维码关注我们,更多干货等你来拿!