海归学者发起的公益学术平台
分享信息,整合资源
交流学术,偶尔风月

在材料科学领域,机器学习已成为加速新材料开发的有力工具。然而,一个长期存在的困境是:研究者构建的机器学习模型往往难以被他人直接使用,存在严重的"模型不可共享"问题。以多主元高温合金(MPESAs)设计为例,虽然已有研究利用机器学习预测相形成,但这些模型通常不公开原始数据、算法参数或代码,导致其他研究者无法复现和应用。这种局限性阻碍了机器学习在材料科学中的进一步发展。
Fig.1Workflow of the present work.
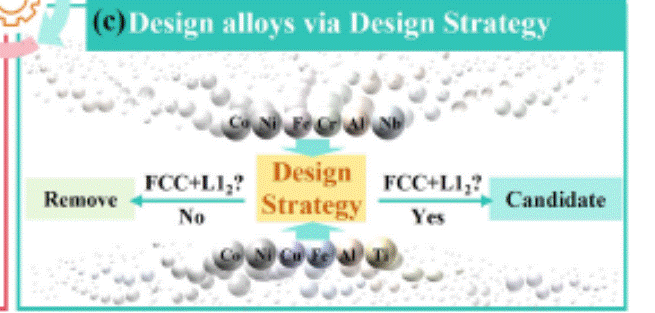
哈尔滨工业大学(深圳)材料科学与工程学院刘兴军教授和姚志富博士团队提出了一种创新解决方案——将机器学习模型知识转化为可理解的材料设计规则。他们首先构建了两个分类模型:一个用于预测L12相形成(准确率95.42%),另一个用于预测其他杂相析出(准确率85.82%)。随后,研究团队采用Shapley加性解释(SHAP)方法,从这些"黑箱"模型中提取关键知识,并将其转化为明确的设计规则。最重要的是,这种方法完全规避了传统机器学习模型共享的技术障碍。
Fig.2 The SHAP values of elements. The blue and orange colors for Target-A and gray and yellow for Target-B.The common region between orange and yellow, representing the optimal value range of the “FCC+L12” dual-phase microstructure.
Fig.3 The SHAP values of empirical parameters. The blue and orange colors for Target-A and gray and yellow for Target-B.
通过这种方法,研究团队确立了MPESAs中形成"FCC+L12"双相微观结构的通用设计策略:VEC > 8,-16.0 < ΔHmix< -9.7 J mol-1 K-1,以及1671 Tm < 1822 K。令人惊叹的是,基于这一策略随机选择的12种不同成分合金,在实验制备后全部展现出理想的"FCC+L12"双相结构。其中一种合金更是表现出1218°C的高固溶温度和7.77 g cm-3的超低密度,性能优于大多数已知MPESAs。
Fig.4The measured results of density and L12-phase solvus temperature of these 12 alloys. (a) DSC heating curve of 12 alloy. (b) Densities and L12-phase solvus temperatures of the 12 designed MPESAs. (c) Comparison of L12-phase solvus temperatures and densities of various L12-strengthened alloys
这项研究的意义不仅在于开发出高效的MPESAs设计策略,更开创了一种将机器学习知识转化为可共享设计规则的新范式。刘兴军教授指出:"我们的方法使任何材料设计师都能直接应用这些设计规则,无需依赖复杂的机器学习模型。"这种方法可推广到其他材料体系的设计中,为解决机器学习在材料科学中的共享难题提供了普适性方案。该文近期发表于npj Computationa
l Materials 11:99(2025),英文标题与摘要如下,点击左下角“阅读原文”可以自由获取论文PDF。
Transforming machine learning model knowledge into material insights for multi-principal-element superalloy phase design
Qiuling Tao, Xintong Yang, Longke Bao, Yuexin Zhou, Tao Yang, Yilu Zhao, Rongpei Shi, Zhifu Yao & Xingjun Liu
Machine learning (ML) is a powerful tool for the accelerated design and development of various materials. However, the constructed ML models are often difficult to use by researchers other than the creator, that is, model sharing is a challenge. Here, we propose a method to avoid this issue by transforming the knowledge learned from ML models into material rules to obtain a generic design strategy. Specifically, we take the prediction of phase formation in multi-principal-element superalloys (MPESAs) as an example. First, we construct two classification models using ML algorithms to predict the presence or absence of the L12 phase and other phases, respectively. Then, the Shapley additive explanation method is used to extract knowledge from the models and transform them into understandable material insights. Based on this method, we obtain a generic design strategy for rapidly determining the phase formation of MPESAs, specifically the combination of VEC > 8, −16.0 < ∆Hmix 98%) design of alloys with an “FCC + L12” dual-phase microstructure. We used this strategy to randomly select 12 candidates composed of different elements from the large design space for experimental preparation. The experimental results show that all these alloys exhibit the ideal “FCC + L12” dual-phase microstructure, verifying the accuracy of the design strategy. Notably, one of the alloys has a good combination of high solvus temperature (1218 °C) and very low density (7.77 g‧cm−3), superior to most MPESAs.