点击上方“计算机视觉工坊”,选择“星标”
干货第一时间送达

https://github.com/zjhellofss/KuiperInfer 感谢大家点赞和PR, 这是对我最大的鼓励, 谢谢.现在KuiperInfer已经支持yolov5s的推理啦, 视频记录在这: KuiperInfer支持YoloV5s推理实录视频课程链接(https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1VW4y1V7vp
) ,请一定要配合视频一起观看此课件哦.配套代码
git clone https://github.com/zjhellofss/KuiperCourse.git
git checkout six
PNNX项目 PyTorch Neural Network eXchange(PNNX)是PyTorch模型互操作性的开放标准.PNNX为PyTorch提供了一种开源的模型格式, 它定义了与PyTorch相匹配的数据流图和运算操作, 我们的框架在
PNNX之上封装了一层更加易用和简单的计算图格式. PyTorch训练好一个模型之后, 然后模型需要转换到PNNX格式, 然后PNNX格式我们再去读取, 形成计算图.PNNX帮我做了很多的图优化、算子融合的工作, 所以底层的用它PNNX的话, 我们可以吸收图优化的结果, 后面推理更快.但是我们不直接在项目中用PNNX, 因为别人的工作和自己推理框架开发思路总是有不同的. 所以在这上面封装, 又快速又好用方便, 符合自己的使用习惯. PNNX的使用方法, 我们只是去读取PNNX导出的模型, 然后构建自己一种易用的计算图结构.PNNX由操作数operand(运算数)和operator(运算符号), PNNX::Graph用来管理和操作这两者.操作数(operand), 也可以通过操作数来方向访问到这个数字的产生者和使用者CustomerOperand
Producer: 类型是operator, 表示产生了这个操作数(operand)的运算符(operator). 也就是说这个操作数(operand)是Producer的输出.比如Producer是有个Add, Operand就是对应的Add结果.-
Customer:类型是operator, 表示需要这个操作数是下一个操作的运算符(operator)的输入. 值得注意的是生产者Producer作为产生这个操作数的operator只能有一个, 而消费者Customer可以有多个, 消费者将当前的操作数Operand作为输入. Name: 类型是std::string, 表示这个操作数的名称.Shape: 类型是std::vector , 用来表示操作数的大小.
Operator
Inputs: 类型为std::vector, 表示这个运算符计算过程中所需要的输入操作数(operand)Outputs: 类型为std::vector, 表示这个运算符计算过程中得到的输出操作数(operand)Type, Name 类型均为std::string, 分别表示运算符号的类型和名称Params, 类型为std::map,用于存放该运算符的所有参数(例如对应Convolution operator的
params中将存放stride, padding, kernel size等信息)Attrs, 类型为std::map, 用于存放运算符号所需要的具体权重属性(例如对应Convolution operator的attrs中就存放着卷积的权重和偏移量)
struct RuntimeOperand {
std::string name; /// 操作数的名称
std::vector<int32_t> shapes; /// 操作数的形状
std::vector<std::shared_ptrfloat>>> datas; /// 存储操作数
RuntimeDataType type = RuntimeDataType::kTypeUnknown; /// 操作数的类型, 一般是float
};
对PNNX::operator的封装是RuntimeOperator, 下面会讲具体的PNNX到KuiperInfer计算图的转换过程./// 计算图中的计算节点
struct RuntimeOperator {
~RuntimeOperator();
std::string name; /// 运算符号节点的名称
std::string type; /// 运算符号节点的类型
std::shared_ptr layer; /// 节点对应的计算Layer
std::vector<std::string> output_names; /// 运算符号的输出节点名称
std::shared_ptr output_operands; /// 运算符号的输出操作数
std::map<std::string, std::shared_ptr> input_operands; /// 运算符的输入操作数
std::vector<std::shared_ptr> input_operands_seq; /// 运算符的输入操作数, 顺序排列
std::map<std::string, RuntimeParameter *> params; /// 算子的参数信息
std::map<std::string, std::shared_ptr > attribute; /// 算子的属性信息, 内含权重信息
};
从PNNX计算图到KuiperInfer计算图的过程
1. 加载PNNX的计算图
int load_result = this->graph_->load(param_path_, bin_path_);
2. 获取PNNX计算图中的运算符(operators)
std::vector<:operator> operators = this->graph_->ops;
if (operators.empty()) {
LOG(ERROR) ;
return false;
}
3. 遍历PNNX计算图中的运算符, 构建KuiperInfer计算图
for (const pnnx::Operator *op : operators) {
...
}
4. 初始化RuntimeOperator的输入
初始化RuntimeOperator中的RuntimeOperator.input_operands和RuntimeOperator.input_operands_seq两个属性.通过解析pnnx的计算图来初始化KuiperInfer RuntimeOperator中的输入部分. 简单来说就是从pnnx::inputs转换得到KuiperInfer::operator::inputsstruct RuntimeOperator {
/// 本过程要初始化的两个属性
std::map<std::string, std::shared_ptr> input_operands; /// 运算符的输入操作数
std::vector<std::shared_ptr> input_operands_seq; /// 运算符的输入操作数, 顺序排列
...
}
从PNNX::Operator::Input到KuiperInfer::Operator::Input的转换过程, 代码链接const pnnx::Operator *op = ...
const
std::vector<:operand> &inputs = op->inputs;
if (!inputs.empty()) {
InitInputOperators(inputs, runtime_operator);
}
....
void RuntimeGraph::InitInputOperators(const std::vector<:operand> &inputs,
const std::shared_ptr &runtime_operator) {
// 遍历输入pnnx的操作数类型(operands), 去初始化KuiperInfer中的操作符(RuntimeOperator)的输入.
for (const pnnx::Operand *input : inputs) {
if (!input) {
continue;
}
// 得到pnnx操作数对应的生产者(类型是pnnx::operator)
const pnnx::Operator *producer = input->producer;
// 初始化RuntimeOperator的输入runtime_operand
std::shared_ptr runtime_operand = std::make_shared();
// 赋值runtime_operand的名称和形状
runtime_operand->name = producer->name;
runtime_operand->shapes = input->shape;
switch (input->type) {
case 1: {
runtime_operand->type = RuntimeDataType::kTypeFloat32;
break;
}
case 0: {
runtime_operand->type = RuntimeDataType::kTypeUnknown;
break;
}
default: {
LOG(FATAL) }
}
// runtime_operand放入到KuiperInfer的运算符中
runtime_operator->input_operands.insert({producer->name, runtime_operand});
runtime_operator->input_operands_seq.push_back(runtime_operand);
}
}
5. 初始化RuntimeOperator中的输出
初始化RuntimeOperator.output_names属性. 通过解析PNNX的计算图来初始化KuiperInfer Operator中的输出部分.代码链接简单来说就是从PNNX::outputs到KuiperInfer::operator::outputvoid RuntimeGraph::InitOutputOperators(const std::vector<:operand> &outputs,
const std::shared_ptr &runtime_operator) {
for (const pnnx::Operand *output : outputs) {
if (!output) {
continue;
}
const auto &consumers = output->consumers;
for (const auto &c : consumers) {
runtime_operator->output_names.push_back(c->name);
}
}
}
6. 初始化RuntimeOperator的权重(Attr)属性
KuiperInfer::RuntimeOperator::RuntimeAttributes. Attributes中存放的是operator计算时需要的权重属性, 例如Convolution Operator中的weights和bias.
// 初始化算子中的attribute(权重)
const pnnx::Operator *op = ...
const std::map<std::string, pnnx::Attribute> &attrs = op->attrs;
if (!attrs.empty()) {
InitGraphAttrs(attrs, runtime_operator);
}
void RuntimeGraph::InitGraphAttrs(const std::map<std::string, pnnx::Attribute> &attrs,
const std::shared_ptr &runtime_operator) {
for (const auto &pair : attrs) {
const std::string &name = pair.first;
// 1.得到pnnx中的Attribute
const pnnx::Attribute &attr = pair.second;
switch (attr.type) {
case 1: {
// 2. 根据Pnnx的Attribute初始化KuiperInferOperator中的Attribute
std::shared_ptr runtime_attribute = std::make_shared();
runtime_attribute->type = RuntimeDataType::kTypeFloat32;
// 2.1 赋值权重weight(此处的data是std::vector类型)
runtime_attribute->weight_data = attr.data;
runtime_attribute->shape = attr.shape;
runtime_operator->attribute.insert({name, runtime_attribute});
break;
}
default : {
LOG(FATAL) ;
}
}
}
}
7. 初始化RuntimeOperator的参数(Param)属性
简单来说就是从pnnx::operators::Params去初始化KuiperInfer::RuntimeOperator::Paramsconst std::map<std::string, pnnx::Parameter> ¶ms = op->params;
if (!params.empty()) {
InitGraphParams(params, runtime_operator);
}
KuiperInfer::RuntimeOperator::RuntimeParameter有多个派生类构成, 以此来对应中多种多样的参数, 例如ConvOperator中有std::string类型的参数, padding_mode, 也有像uint32_t类型的kernel_size和padding_size参数, 所以我们需要以多种参数类型去支持他.换句话说, 一个KuiperInfer::operator::Params, param可以是其中的任意一个派生类, 这里我们利用了多态的特性. KuiperInfer::RuntimeOperator::RuntimeParameter具有多种派生类, 如下分别表示为Int参数和Float参数, 他们都是RuntimeParameter的派生类.
std::map<std::string, RuntimeParameter *> params; /// 算子的参数信息
// 用指针来实现多态
struct RuntimeParameter { /// 计算节点中的参数信息
virtual ~RuntimeParameter() = default;
explicit RuntimeParameter(RuntimeParameterType type = RuntimeParameterType::kParameterUnknown) : type(type) {
}
RuntimeParameterType type = RuntimeParameterType::kParameterUnknown;
};
/// int类型的参数
struct RuntimeParameterInt : public RuntimeParameter {
RuntimeParameterInt() : RuntimeParameter(RuntimeParameterType::kParameterInt) {
}
int value = 0;
};
/// float类型的参数
struct RuntimeParameterFloat : public RuntimeParameter {
RuntimeParameterFloat() : RuntimeParameter(RuntimeParameterType::kParameterFloat) {
}
float value = 0.f;
};
从PNNX::param到RuntimeOperator::param的转换过程.代码链接void RuntimeGraph::InitGraphParams(const std::map<std::string, pnnx::Parameter> ¶ms,
const std::shared_ptr &runtime_operator) {
for (const auto &pair : params) {
const std::string &name = pair.first;
const pnnx::Parameter ¶meter = pair.second;
const int type = parameter.type;
// 根据PNNX的Parameter去初始化KuiperInfer::RuntimeOperator中的Parameter
switch (type) {
case int(RuntimeParameterType::kParameterUnknown): {
RuntimeParameter *runtime_parameter = new RuntimeParameter;
runtime_operator->params.insert({name, runtime_parameter});
break;
}
// 在这应该使用派生类RuntimeParameterBool
case int(RuntimeParameterType::kParameterBool): {
RuntimeParameterBool *runtime_parameter = new RuntimeParameterBool;
runtime_parameter->value = parameter.b;
runtime_operator->params.insert({name, runtime_parameter});
break;
}
// 在这应该使用派生类RuntimeParameterInt
case int(RuntimeParameterType::kParameterInt): {
RuntimeParameterInt *runtime_parameter = new RuntimeParameterInt;
runtime_parameter->value = parameter.i;
runtime_operator->params.insert({name, runtime_parameter});
break;
}
case int(RuntimeParameterType::kParameterFloat): {
RuntimeParameterFloat *runtime_parameter = new RuntimeParameterFloat;
runtime_parameter->value = parameter.f;
runtime_operator->params.insert({name, runtime_parameter});
break;
}
case int(RuntimeParameterType::kParameterString): {
RuntimeParameterString *runtime_parameter = new RuntimeParameterString;
runtime_parameter->value = parameter.s;
runtime_operator->params.insert({name, runtime_parameter});
break;
}
case int(RuntimeParameterType::kParameterIntArray): {
RuntimeParameterIntArray *runtime_parameter = new RuntimeParameterIntArray;
runtime_parameter->value = parameter.ai;
runtime_operator->params.insert({name, runtime_parameter});
break;
}
case int(RuntimeParameterType::kParameterFloatArray): {
RuntimeParameterFloatArray *runtime_parameter = new RuntimeParameterFloatArray;
runtime_parameter->value = parameter.af;
runtime_operator->params.insert({name, runtime_parameter});
break;
}
case int(RuntimeParameterType::kParameterStringArray): {
RuntimeParameterStringArray *runtime_parameter = new RuntimeParameterStringArray;
runtime_parameter->value = parameter.as;
runtime_operator->params.insert({name, runtime_parameter});
break;
}
default: {
LOG(FATAL) ;
}
}
}
}
8. 初始化成功
将通过如上步骤初始化好的KuiperInfer::RuntimeOperator存放到一个vector中this->operators_.push_back(runtime_operator);
我们先准备好了如下的一个计算图(准备过程不是本节的重点, 读者直接使用即可), 存放在tmp目录中, 它由两个卷积, 一个Add(expression)以及一个最大池化层组成.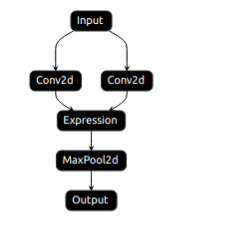 img
imgTEST(test_runtime, runtime1) {
using namespace kuiper_infer;
const std::string ¶m_path = "./tmp/test.pnnx.param";
const std::string &bin_path = "./tmp/test.pnnx.bin";
RuntimeGraph graph(param_path, bin_path);
graph.Init();
const auto operators = graph.operators();
for (const auto &operator_ : operators) {
LOG(INFO) }
}
如上为一个测试函数, Init就是我们刚才分析过的一个函数, 它定义了从PNNX计算图到KuiperInfer计算图的过程.I20230107 11:53:33.033838 56358 test_main.cpp:13] Start test...
I20230107 11:53:33.034411 56358 test_runtime1.cpp:17] type: pnnx.Input name: pnnx_input_0
I20230107 11:53:33.034421 56358 test_runtime1.cpp:17] type: nn.Conv2d name: conv1
I20230107 11:53:33.034425 56358 test_runtime1.cpp:17] type: nn.Conv2d name: conv2
I20230107 11:53:33.034430 56358 test_runtime1.cpp:17] type: pnnx.Expression name: pnnx_expr_0
I20230107 11:53:33.034435 56358 test_runtime1.cpp:17] type: nn.MaxPool2d name: max
I20230107 11:53:33.034440 56358 test_runtime1.cpp:17] type: pnnx.Output name: pnnx_output_0
可以看出, Init函数最后得到的结果和图1中定义的是一致的. 含有两个Conv层, conv1和
conv2, 一个add层Expression以及一个最大池化MaxPool2d层.干货下载与学习
后台回复:巴塞罗那自治大学课件,即可下载国外大学沉淀数年3D Vison精品课件
后台回复:计算机视觉书籍,即可下载3D视觉领域经典书籍pdf
后台回复:3D视觉课程,即可学习3D视觉领域精品课程
计算机视觉工坊精品课程官网:3dcver.com
8.从零搭建一套结构光3D重建系统[理论+源码+实践]
重磅!粉丝学习交流群已成立
交流群主要有3D视觉、CV&深度学习、SLAM、三维重建、点云后处理、自动驾驶、多传感器融合、CV入门、三维测量、VR/AR、3D人脸识别、医疗影像、缺陷检测、行人重识别、目标跟踪、视觉产品落地、视觉竞赛、车牌识别、硬件选型、ORB-SLAM系列源码交流、深度估计、TOF、求职交流等方向。扫描以下二维码,添加小助理微信(dddvisiona),一定要备注:研究方向+学校/公司+昵称,例如:”3D视觉 + 上海交大 + 静静“。请按照格式备注,可快速被通过且邀请进群。原创投稿也请联系。

▲长按加微信群或投稿,微信号:dddvisiona
3D视觉从入门到精通知识星球:针对3D视觉领域的视频课程(三维重建系列、三维点云系列、结构光系列、手眼标定、相机标定、激光/视觉SLAM、自动驾驶等)、源码分享、知识点汇总、入门进阶学习路线、最新paper分享、疑问解答等进行深耕,更有各类大厂的算法工程人员进行技术指导。与此同时,星球将联合知名企业发布3D视觉相关算法开发岗位以及项目对接信息,打造成集技术与就业为一体的铁杆粉丝聚集区,4000+星球成员为创造更好的AI世界共同进步,知识星球入口: