基于图深度学习的多空间依赖性表征及地下水位预测
吴映涵,梅钢*,邵凯旋,徐能雄,彭建兵
中国地质大学(北京)工程技术学院
地下水是一种重要基础资源,准确预测地下水位对于地下水的可持续管理至关重要。尽管现有方法已成功将空间依赖关系集成到地下水预报中,但它们通常侧重于单一类型的空间依赖关系。基于距离的图表提供了空间关联的合理初始表征,但通常假设水文连通性随物理接近程度的接近而下降。这一假设过度简化了由多种互补空间依赖关系(例如物理的邻近性、水文连接和共享环境特征)支配的系统,限制了对空间依赖关系如何影响地下水动态的理解。本研究中从多个角度表征了地下水的空间依赖性,并运用基于图结构数据的深度学习方法,研究了其对地下水动态预测结果的影响。描述多空间依赖性有助于提高对地下水动态的理解,并揭示监测点之间的潜在关联。
本研究探究了考虑多空间依赖性对于地下水位预测的影响,有助于理解区域监测网络中复杂空间依赖结构的附加价值。相关研究发表在《Journal of Geophysical Research: Machine Learning and Computation》上。Accurate forecasting for groundwater levels is essential for water resource management and sustainable development. Regional variations in groundwater levels exhibit a complex spatial dependency structure due to the physical proximity of monitoring wells, hydrological connectivity, and shared environmental characteristics. However, existing research has mostly overlooked the multiple spatial dependencies between monitoring wells, limiting the understanding of the added value that graph-based models bring to groundwater dynamics prediction. In this study, we characterize spatial dependencies of groundwater from multiple perspectives and investigate the impact on the forecasting results of groundwater dynamics using graph-based deep learning. Characterizing spatial dependencies helps improve the understanding of groundwater dynamics, but its effectiveness in enhancing prediction accuracy depends on the characteristics of spatial interactions. Graph neural networks facilitate learning from diverse spatial associations, allowing for a more comprehensive representation of spatial dependencies and uncovering potential connections between monitoring wells. Results based on real data sets contribute to understanding how multiple spatial dependencies influence groundwater level forecasting. Our research provides insights into exploiting potential spatial dependencies in similarly complex and highly interconnected earth systems.
1. 图神经网络能够表征多空间依赖性并用于地下水位预测。
2. 描述多空间依赖性有助于理解地下水的动态变化。
3. 考虑多空间依赖性的图方法能够揭示地下水位动态时间序列中的潜在关联
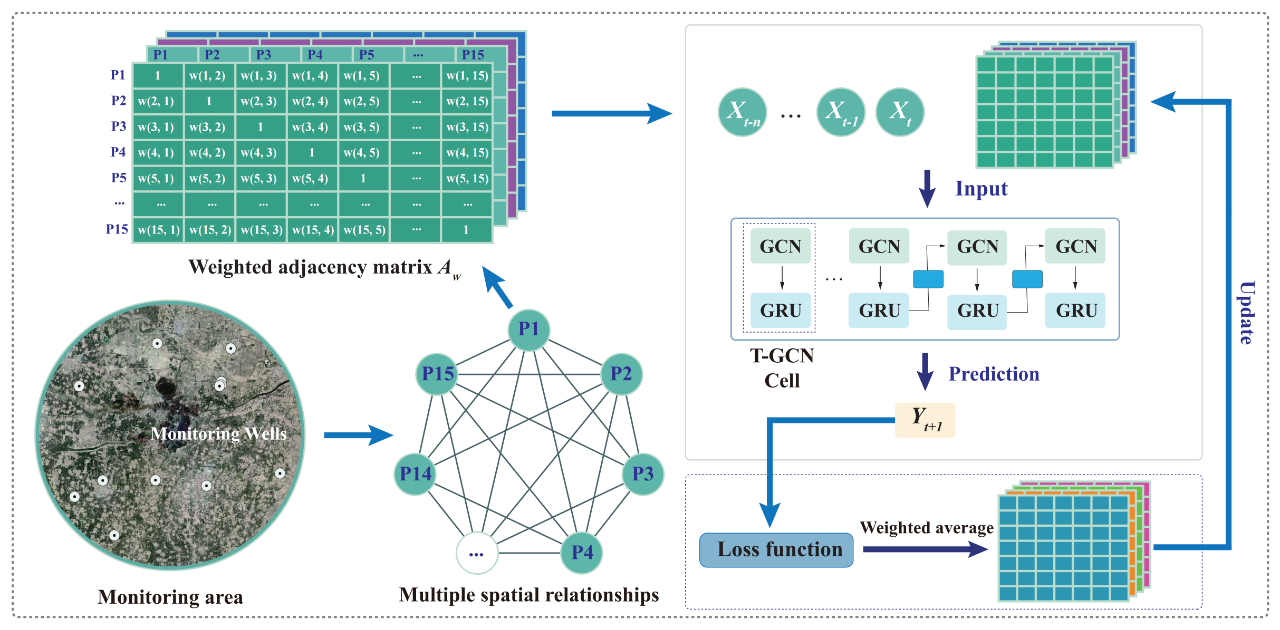
图1:使用时间图卷积网络表征和耦合多空间依赖关系实现地下水位时空预测的过程。
图2:考虑多空间依赖性的图神经网络利用监测点的空间信息相应地调整其预测。
图3:层次聚类展示了在整体时序模式上具有相似性的监测点集合,揭示了区域内具有共性水文动态的子集。
图4:考虑多空间依赖性的图深度学习能够揭示地下水位动态时间序列中的潜在关联。
1. 表征多空间依赖性有助于更好地理解地下水动态,但其提高预测准确性的效果取决于空间交互特征。2. 基于图的深度学习能够从各种空间关联中有效学习,从而更全面地表示空间依赖关系。但对于那些局部异常或特征显著不同的监测井,部分依赖可能引入噪声或无关信息。
3. 考虑多空间依赖性的图深度学习能够揭示地下水位动态时间序列中的潜在关联。Wu, Yinghan., Mei, Gang., Shao, Kaixuan., Xu, Nengxiong., & Peng, Jianbing. (2025). Forecasting groundwater level by characterizing multiple spatial dependencies of environmental factors using graph-based deep learning. Journal of Geophysical Research: Machine Learning and Computation, 2, e2024JH000520.
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JH000520
或点击下方阅读原文