作者:Kamil Polak 翻译:刘思婧 校对:孙韬淳本文约2700字,建议阅读5分钟
本文为大家介绍了主题建模的概念、LDA算法的原理,示例了如何使用Python建立一个基础的LDA主题模型,并使用pyLDAvis对主题进行可视化。
引言
主题建模包括从文档术语中提取特征,并使用数学结构和框架(如矩阵分解和奇异值分解)来生成彼此可区分的术语聚类(cluster)或组,这些单词聚类继而形成主题或概念。主题建模是一种对文档进行无监督分类的方法,类似于对数值数据进行聚类。这些概念可以用来解释语料库的主题,也可以在各种文档中一同频繁出现的单词之间建立语义联系。发现数据集中隐藏的主题;
将文档分类到已经发现的主题中;
使用分类来组织/总结/搜索文档。
潜在语义索引(Latent semantic indexing)
潜在狄利克雷分配(Latent Dirichlet Allocation,LDA)
非负矩阵分解(Non-negative matrix factorization,NMF)
在本文中,我们将重点讨论如何使用Python进行LDA主题建模。具体来说,我们将讨论:什么是潜在狄利克雷分配(LDA, Latent Dirichlet allocation)?
潜在狄利克雷分配(LDA, Latent Dirichlet allocation)是一种生成概率模型(generative probabilistic model),该模型假设每个文档具有类似于概率潜在语义索引模型的主题的组合。简而言之,LDA背后的思想是,每个文档可以通过主题的分布来描述,每个主题可以通过单词的分布来描述。LDA算法如何工作?
注意:LDA不关心文档中单词的顺序。通常,LDA使用词袋特征(bag-of-word feature)表示来代表文档。1. 对于每个文档,随机将每个单词初始化为K个主题中的一个(事先选择K个主题);3. 考虑所有其他单词及其主题分配,以概率P(T | D)´ P(W | T) 将单词W与主题T重新分配。LDA主题模型的图示如下。
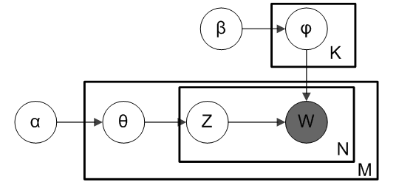

下图直观地展示了每个参数如何连接回文本文档和术语。假设我们有M个文档,文档中有N个单词,我们要生成的主题总数为K。图中的黑盒代表核心算法,它利用前面提到的参数从文档中提取K个主题。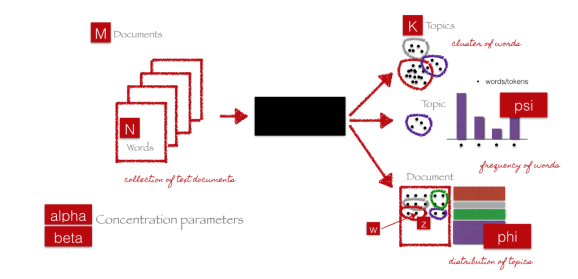
如何使用Python建立LDA主题模型
我们将使用Gensim包中的潜在狄利克雷分配(LDA)。首先,我们需要导入包。核心包是re、gensim、spacy和pyLDAvis。此外,我们需要使用matplotlib、numpy和panases以进行数据处理和可视化。1. import re2. import numpy as np3. import pandas as pd4. from pprint import pprint5. 6. # Gensim
7. import gensim8. import gensim.corpora as corpora9. from gensim.utils import simple_preprocess10. from gensim.models import CoherenceModel11. 12. # spacy for lemmatization13. import spacy14. 15. # Plotting tools16. import pyLDAvis17. import pyLDAvis.gensim # don't skip this18. import matplotlib.pyplot as plt19. %matplotlib inline20. 21. # Enable logging for gensim - optional22. import logging23. logging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s : %(levelname)s : %(message)s', level=logging.ERROR)24. 25. import warnings26. warnings.filterwarnings("ignore",category=DeprecationWarning)
像am/is/are/of/a/the/but/…这样的词不包含任何关于“主题”的信息。因此,作为预处理步骤,我们可以将它们从文档中移除。要做到这一点,我们需要从NLT导入停用词。还可以通过添加一些额外的单词来扩展原始的停用词列表。1. # NLTK Stop words2. from nltk.corpus import stopwords3. stop_words = stopwords.words('english')4. stop_words.extend(['from', 'subject', 're', 'edu', 'use'])
在本教程中,我们将使用20个新闻组数据集,其中包含来自20个不同主题的大约11k个新闻组帖子。这可以作为newsgroups.json获得。1. # Import Dataset2. df = pd.read_json('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/newsgroups.json')3. print(df.target_names.unique())4. df.head()

在我们开始主题建模之前,需要清理数据集。首先,删除电子邮件链接、多余的空格和换行符。1. # Convert to list2. data = df.content.values.tolist()3. 4. # Remove Emails5. data = [re.sub('\S*@\S*\s?', '', sent) for sent in data]6. 7. # Remove new line characters8. data = [re.sub('\s+', ' ', sent) for sent in data]9. 10. # Remove distracting single quotes11. data = [re.sub("\'", "", sent) for sent in data]12. 13. pprint(data[:1])

让我们把每个句子标记成一个单词列表,去掉标点符号和不必要的字符。1. def sent_to_words(sentences):2. for sentence in sentences:3. yield(gensim.utils.simple_preprocess(str(sentence), deacc=True)) # deacc=True removes punctuations4. 5. data_words = list(sent_to_words(data))6. 7. print(data_words[:1])

创建二元(Bigram)模型和三元(Trigram)模型1. # Build the bigram and trigram models2. bigram = gensim.models.Phrases(data_words, min_count=5, threshold=100) # higher threshold fewer phrases.3. trigram = gensim.models.Phrases(bigram[data_words], threshold=100) 4. 5. # Faster way to get a sentence clubbed as a trigram/bigram6. bigram_mod = gensim.models.phrases.Phraser(bigram)7. trigram_mod = gensim.models.phrases.Phraser(trigram)8. 9. # See trigram example
10. print(trigram_mod[bigram_mod[data_words[0]]])
删除停用词(stopword),建立二元模型和词形还原(Lemmatize)在这一步中,我们分别定义了函数以删除停止词、建立二元模型和词形还原,并且依次调用了这些函数。
1. # Define functions for stopwords, bigrams, trigrams and lemmatization2. def remove_stopwords(texts):3. return [[word for word in simple_preprocess(str(doc)) if word not in stop_words] for doc in texts]4. 5. def make_bigrams(texts):6. return [bigram_mod[doc] for doc in texts]7. 8. def make_trigrams(texts):9. return [trigram_mod[bigram_mod[doc]] for doc in texts]10. 11. def lemmatization(texts, allowed_postags=['NOUN', 'ADJ', 'VERB', 'ADV']):12. """https://spacy.io/api/annotation"""13. texts_out = []14. for sent in texts:15. doc = nlp(" ".join(sent)) 16. texts_out.append([token.lemma_ for token in doc if token.pos_ in allowed_postags])17. return texts_out
1. # Remove Stop Words2. data_words_nostops = remove_stopwords(data_words)3. 4. # Form Bigrams
5. data_words_bigrams = make_bigrams(data_words_nostops)6. 7. # Initialize spacy 'en' model, keeping only tagger component (for efficiency)8. # python3 -m spacy download en9. nlp = spacy.load('en', disable=['parser', 'ner'])10. 11. # Do lemmatization keeping only noun, adj, vb, adv12. data_lemmatized = lemmatization(data_words_bigrams, allowed_postags=['NOUN', 'ADJ', 'VERB', 'ADV'])13. 14. print(data_lemmatized[:1])

Gensim为文档中的每个单词创建一个唯一的id,但是在此之前,我们需要创建一个字典和语料库作为模型的输入。1. # Create Dictionary2. id2word = corpora.Dictionary(data_lemmatized)3. 4. # Create Corpus5. texts = data_lemmatized6. 7. # Term Document Frequency8. corpus = [id2word.doc2bow(text) for text in texts]9. 10. # View11. print(corpus[:1])

现在我们准备进入核心步骤,使用LDA进行主题建模。让我们开始建立模型。我们将建立20个不同主题的LDA模型,其中每个主题都是关键字的组合,每个关键字在主题中都具有一定的权重(weightage)。1. # Build LDA model2. lda_model = gensim.models.ldamodel.LdaModel(corpus=corpus,3. id2word=id2word,4. num_topics=20, 5. random_state=100,6. update_every=1,7. chunksize=100,8. passes=10,9. alpha='auto',10. per_word_topics=True)
我们可以可视化每个主题的关键词和每个关键词的权重(重要性)。1. # Print the Keyword in the 10 topics
2. pprint(lda_model.print_topics())3. doc_lda = lda_model[corpus]



计算模型困惑度(Perplexity)和一致性分数(Coherence Score)模型困惑度是对概率分布或概率模型预测样本好坏的一种度量。主题一致性通过测量主题中得分高的单词之间的语义相似度来衡量单个主题的得分。简而言之,它们提供了一种方便的方法来判断一个给定的主题模型有多好。1. # Compute Perplexity2. print('\nPerplexity: ', lda_model.log_perplexity(corpus)) # a measure of how good the model is. lower the better.3. 4. # Compute Coherence Score5. coherence_model_lda = CoherenceModel(model=lda_model, texts=data_lemmatized, dictionary=id2word, coherence='c_v')6. coherence_lda = coherence_model_lda.get_coherence()7. print('\nCoherence Score: ', coherence_lda)

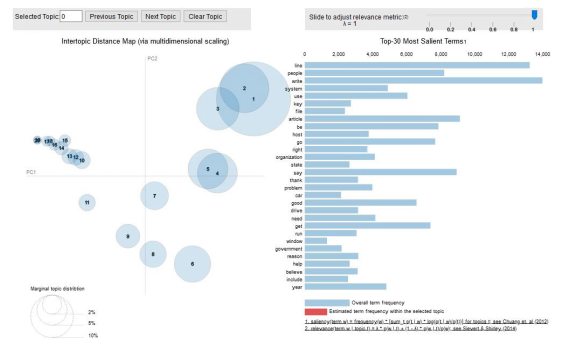
现在,我们可以检查生成的主题和相关的关键词。最好的方法是使用pyLDAvis可视化我们的模型。
pyLDAvis旨在帮助用户在一个适合文本数据语料库的主题模型中解释主题。它从拟合好的的线性判别分析主题模型(LDA)中提取信息,以实现基于网络的交互式可视化。1. # Visualize the topics2. pyLDAvis.enable_notebook()3. vis = pyLDAvis.gensim.prepare(lda_model, corpus, id2word)4. vis
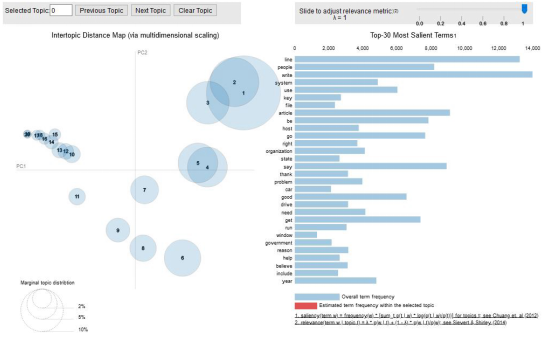
简要地解释一下结果:左手边的每个气泡代表一个话题。气泡越大,该主题就越盛行。根据经验,一个好的主题模型会有大的、不重叠的气泡。我们也可以点击右边的侧边工具条,以调整阿尔法(alpha)参数。结语
主题建模是自然语言处理的主要应用之一。本文的目的是解释什么是主题建模,以及如何在实际使用中实现潜在狄利克雷分配(LDA)模型。
为此,我们深入研究了LDA的原理,使用Gensim包中的LDA构建了一个基础的主题模型,并使用pyLDAvis对主题进行了可视化。希望您喜欢该文并有所收获。
References:
Jelodar, H., Wang, Y., Yuan, C. et al. Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) and topic modeling: models, applications, a survey. Multimed Tools Appl 78, 15169–15211 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6894-4https://jovian.ai/outlink?url=https%3A%2F%2Fdoi.org%2F10.1007%2Fs11042-018-6894-4D. Sarkar, Text Analytics with Python. A Practical Real-World Approach to Gaining Actionable Insights from Your Datahttps://www.machinelearningplus.com/nlp/topic-modeling-gensim-python/https://jovian.ai/outlink?url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.machinelearningplus.com%2Fnlp%2Ftopic-modeling-gensim-python%2F
https://towardsdatascience.com/topic-modelling-in-python-with-nltk-and-gensim-4ef03213cd21https://jovian.ai/outlink?url=https%3A%2F%2Ftowardsdatascience.com%2Ftopic-modelling-in-python-with-nltk-and-gensim-4ef03213cd21https://towardsdatascience.com/end-to-end-topic-modeling-in-python-latent-dirichlet-allocation-lda-35ce4ed6b3e0https://jovian.ai/outlink?url=https%3A%2F%2Ftowardsdatascience.com%2Fend-to-end-topic-modeling-in-python-latent-dirichlet-allocation-lda-35ce4ed6b3e0https://towardsdatascience.com/latent-dirichlet-allocation-lda-9d1cd064ffa2https://towardsdatascience.com/light-on-math-machine-learning-intuitive-guide-to-latent-dirichlet-allocation-437c81220158http://blog.echen.me/2011/08/22/introduction-to-latent-dirichlet-allocation/译者简介:刘思婧,清华大学新闻系研一在读,数据传播方向。文理兼爱,有点小情怀的数据爱好者。希望结识更多不同专业、不同专长的伙伴,拓宽眼界、优化思维、日日自新。版权声明:本号内容部分来自互联网,转载请注明原文链接和作者,如有侵权或出处有误请和我们联系。
合作请加QQ:365242293
数据分析(ID : ecshujufenxi )互联网科技与数据圈自己的微信,也是WeMedia自媒体联盟成员之一,WeMedia联盟覆盖5000万人群。