海归学者发起的公益学术平台
分享信息,整合资源
交流学术,偶尔风月

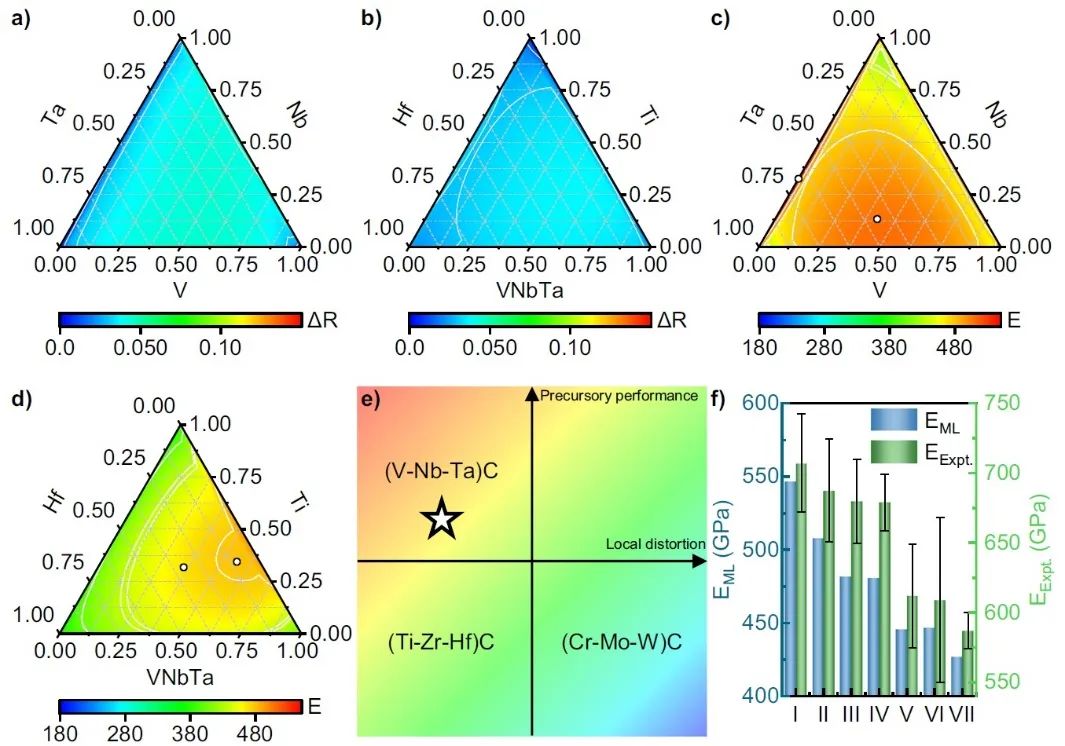
旨在解决能源危机和气候变化的新兴技术对所需的结构材料提出了严苛的要求。高熵合金的概念为设计高强度材料带来了新机遇。尽管MTMCs有望解决上述挑战,但其庞大的组成空间带来了高昂的设计成本,使通过实验和第一性原理计算来扫描并微调MTMCs成分难以实现。此外,对理解高熵组分条件下MTMCs的价电子浓度(VEC)、混合规则(ROM)和结构畸变的作用仍存在显著不足。
来自香港城市大学机械工程系的赵仕俊教授和湖南大学吴正刚教授领导的团队利用数据驱动的方法设计高性能MTMCs。该团队精心构建了包含三元、四元、五元和六元MTMCs的从头算数据库,在此基础上建立了高精度且泛化能力良好的机器学习模型。而后,基于训练好的机器学习模型,对等原子和非等原子MTMCs进行了高通量预测。他们的发现显示,许多MTMCs的机械性能并不遵循混合规则。此外,MTMCs的机械强度与VEC只存在弱相关关系。通过进一步的几何和电子结构分析,他们提出元素适应岩盐结构的能力是理解MTMCs机械性能的重要因素。他们进一步阐述了高性能MTMC设计的规则,通过该规则推荐一些成分,即在阳离子亚晶格中含有V、Nb或Ta的MTMCs具有高模量的特点。这些结论得到了实验的进一步支持,表明了该团队所开发的机器学习模型和提出的设计原则的有效性。
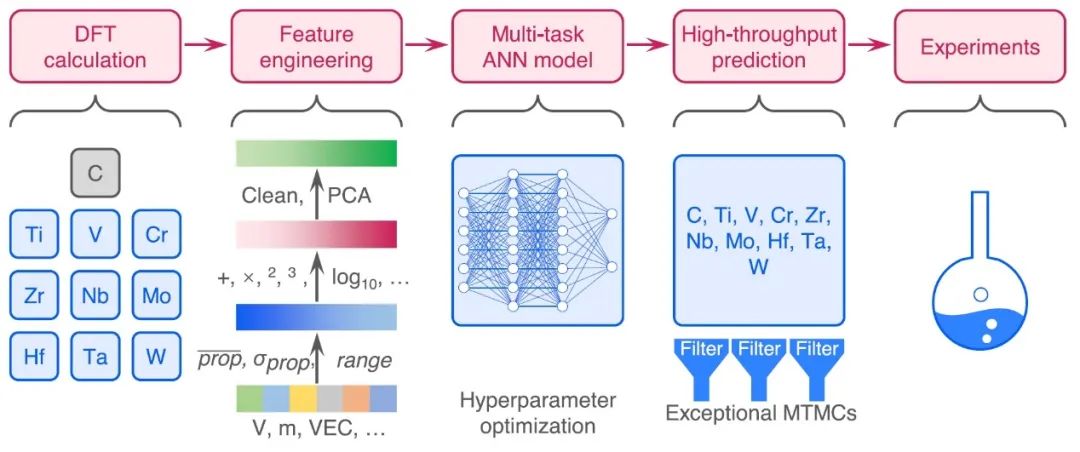
Fig. 1 | Machine-learning workflow.
该文近期发表于npj Computational Materials 10: 1162 (2024),英文标题与摘要如下,点击左下角“阅读原文”可以自由获取论文PDF。
Local-distortion-informed exceptional multicomponent transition-metal carbides uncovered by machine learning
Jun Zhang, Liu He, Yaoxu Xiong, Shasha Huang, Biao Xu, Shihua Ma, Xuepeng Xiang, Haijun Fu, Jijung Kai, Zhenggang Wu & ShijunZhao
Developing high-performance multicomponent ceramics, which are promising in solving challenges posed by emerging technologies, shows grand difficulties because of the immense compositional space and complex local distortions. In this work, an accurate machine learning (ML) model built upon an ab initio database is developed to predict the mechanical properties and structural distortions of multicomponent transition metal carbides (MTMCs). The compositional space of MTMCs is thoroughly explored by the well-trained model. Combined with electronic and geometrical analysis, we show that the elemental adaptability to the rock-salt structure elegantly elucidates the mechanical characteristics of MTMCs, and such adaptability can be quantified by local lattice distortions. We further establish new design principles for high-strength MTMCs, and V–Nb–Ta-based MTMCs are recommended, which are validated by the present experiments. The proposed model and design philosophy pave a broad avenue for the rational design of MTMCs with exceptional properties.